FIGURE 2.
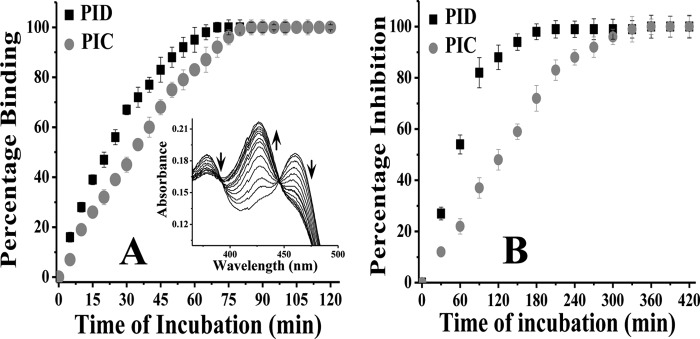
Comparative affinity for iNOSfl (A) and inhibition potency (B) of PIC and PID. A, 10 μm of each compound (PID and PIC) was added to 2 μm of the enzyme in a cuvette, and the spectrum was recorded in situ during such incubation to measure the degree of inhibitor binding at 427 nm in a time-dependent manner at 37 °C. The inset shows typical spectra for time-dependent shift in absorbance at 427 nm against a decrease at 460 nm in the iNOSfl protein free of Arg and H4B due to PID binding. Percentage binding was determined as a ratio of the change in absorbance Δ(460–427) nm versus time of incubation with inhibitor against that recorded for the inhibitor-untreated enzyme. B, aliquots from a similar reaction between the iNOSfl protein and PIC/PID as shown in A were collected at the indicated time points (x axis) after incubation with PIC/PID and the NO synthesis assay performed at 37 °C for 30 min and the generated NO measured as a function of nitrite content by extrapolation of the nitrite standard curve recorded at 550 nm through Griess reaction. The percentage inhibition due to PIC/PID treatment was then determined as a ratio of the drop in activity with respect to the wild type iNOSfl against time of incubation with the inhibitors. For each assay, the corresponding changes obtained for untreated controls, where the iNOS was incubated with the reaction buffer in the absence of the inhibitor under identical conditions and time, as the inhibitor-treated counterparts, were subtracted from the inhibitor-treated values to arrive at the actual values obtained due to the effect of the inhibitors and plotted against time of incubation. Data shown in A and B are mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments.
