FIGURE 1.
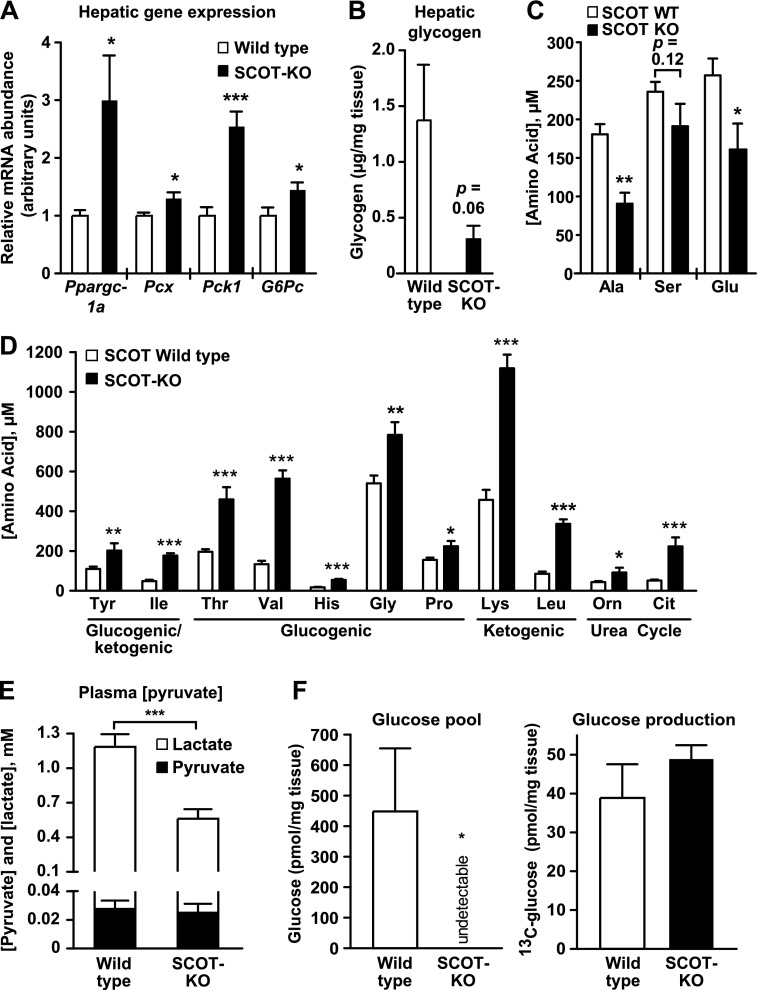
Absence of extrahepatic ketone body oxidation engages an hepatic gluconeogenic program in neonatal mice. A, relative mRNA abundance of encoded mediators of pyruvate metabolism and gluconeogenesis in livers of P1 mice. n = 5/group. B, liver glycogen content (μg of glycogen/mg of tissue) in P1 neonates. n = 8/group. p = 0.06 by Student's t test. C, blood alanine, serine, and glutamate concentrations (micromolar) in P1 mice. n = 5–7/group. D, circulating amino acid concentrations (micromolar) in blood of P1 mice. n = 5–10/group. E, plasma pyruvate pool (pyruvate + lactate) in P1 mice. n = 8–11/group. F, endogenous hepatic glucose concentration (left) and accumulated [13C]glucose in livers (right) of P1 mice that had been injected with [3-13C]pyruvate (10 μmol/g of body weight) 30 min prior to collection of tissues and generation of extracts for NMR. n = 4/group. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 by Student's t test. Error bars, S.E.