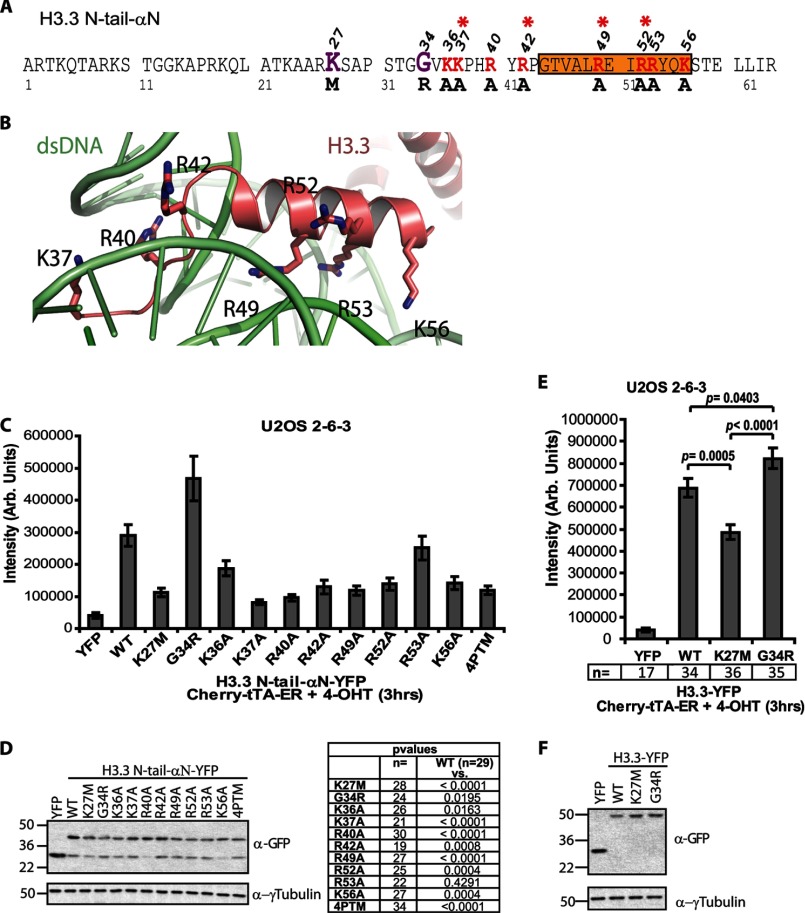
FIGURE 6.
Quantitative single-cell image analysis of H3.3 recruitment to the activated transgene array in U2OS cells. A, diagram of the amino acid sequence of the H3.3 N-tail-αN construct showing the locations of the point mutations analyzed in the single-cell recruitment assay. The locations of the pediatric glioblastoma driver mutations, K27M and G34R, are shown in purple. The amino acids converted to alanine are shown in red. Asterisks mark the amino acids mutated in the four-point mutant (4PTM) construct. Orange shading demarcates the αN helix. B, crystal structure of histone H3 from amino acids 37–60 (salmon) in relation to dsDNA (green) in the nucleosome (Protein Data Bank code 3LJA). The lysine and arginine residues changed to alanine are numbered. C, quantitative single-cell image analysis of the total intensity of the YFP-tagged H3.3 N-tail-αN constructs at the activated transgene array. Error bars, S.E. n and p values, calculated using unpaired t test, are presented in the chart below. D, Western blot analysis of the YFP-tagged H3.3 N-tail-αN constructs using a GFP antibody. Tubulin is used as a loading control. E, quantitative single-cell image analysis of the total intensity of the YFP-tagged H3.3 constructs at the activated transgene array. Error bars, S.E. n values are presented below the graph, and p values, calculated using unpaired t test, are presented in the graph. F, Western blot analysis of full-length YFP-tagged H3.3 constructs using a GFP antibody. Tubulin is used as a loading control.