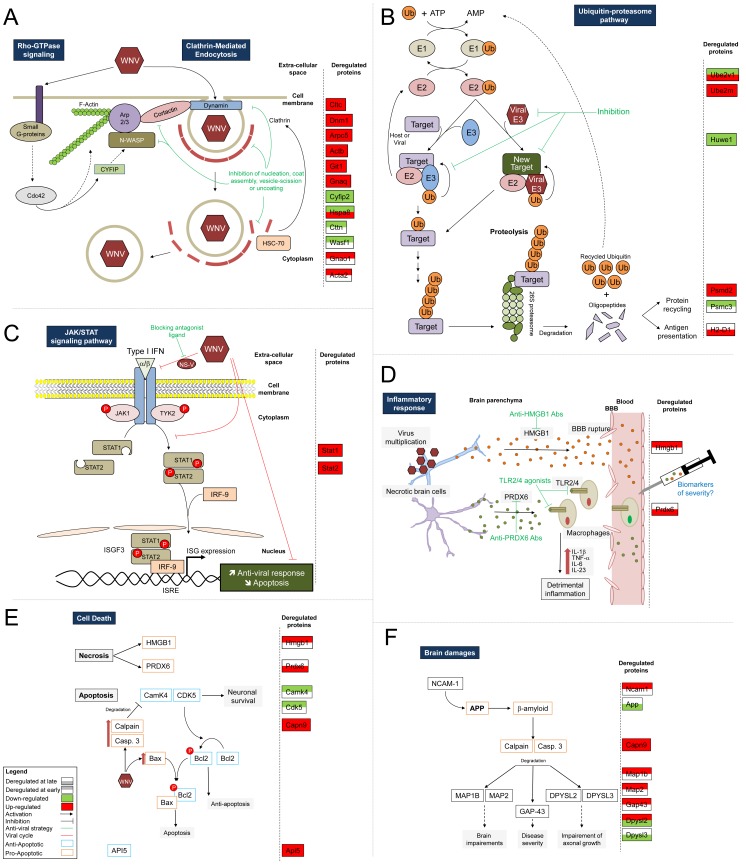
Figure 5. Schematic illustration of key pathways or biological functions altered during the course of WNV infection.
Host proteins that were found to be significantly differentially regulated by proteomic approaches were located in relevant pathways based on the IPA database results and a careful reading of published literature. The proteins that were determined to be differentially regulated in our study are indicated in the right portion of each panel, according to the different time-point comparisons. Several functions were altered during the course of WNV-infection in the mice brain, including: (A) The cytoskeleton remodeling associated with virus circulation as evidenced by the WNV hijacking of the clathrin-mediated endocytosis pathway (CME) and Rho GTPase signaling. (B) The perturbations of the protein ubiquitination pathway allowing viral proteins to avoid degradation and/or antigen presentation. (C) The regulation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway corresponding to an evasion mechanism against activation of the antiviral response. (D) The kinetic modulation of the inflammatory response leading to brain injuries. (E) Cell death comprising neuronal necrosis and apoptotic phenomena. (F) The brain damage reflected by the abundance variation of numerous proteins involved in the deterioration of neurological functions. Known partners of identified differentially regulated molecules are indicated. Anti-viral strategies and potential biomarker candidates associated with the severity of clinical evolution are suggested as indicated in green and blue, respectively. A legend is shown in the bottom left corner. Abbreviations of IPA-uploaded proteins are listed in Tables 1, S4 and S5. The others are listed as follows: Bax, Bcl2-associated X protein; BBB, blood-brain barrier; Bcl2, B-cell lymphoma 2; Casp.3, Caspase 3; Cdc42, cell division cycle 42; E1 and E2, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme; E3, ubiquitin protein ligase; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; IRF9, interferon regulatory factor 9; ISG, interferon-stimulated gene; ISGF3, IFN stimulated gene factor 3; ISRE, interferon-stimulated response element; JAK1, Janus kinase 1; NS-V, non-structural viral protein; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; TYK2, tyrosine kinase 2; Ub, ubiquitin.