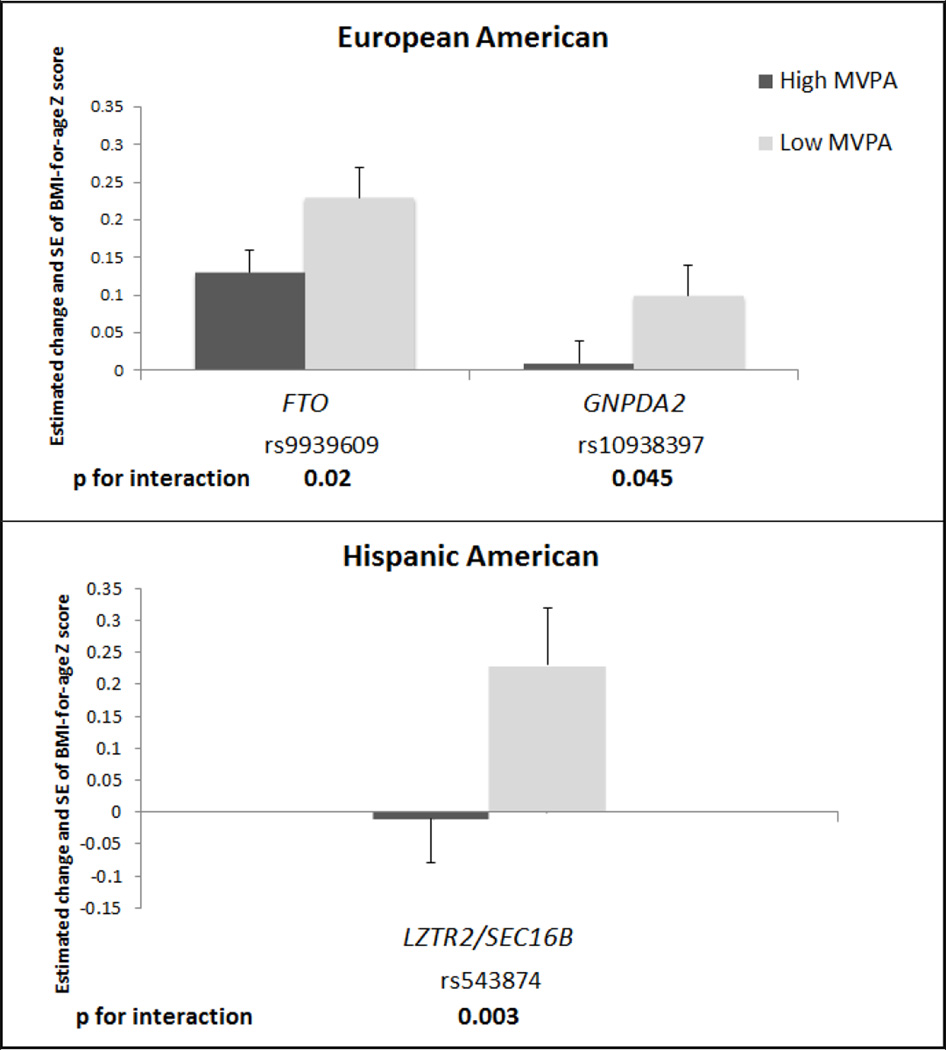
Figure 2.
Estimated effects1 for BMI-for-age Z score per one copy of risk allele in the 3 SNPs with nominally significant interactions2 by high versus low MVPA3 and across European American and Hispanic American subpopulations
Abbreviation: MVPA moderate to vigorous physical activity, EA, European American, AA, African American, HA, Hispanic American
1 MVPA stratified model: Multi-level model of adolescent BMI-for-age Z score regressed on SNP, controlling for age, sex, current smoking (at least one cigarette every day for 30 days), screen time (hours of screen time from television, video, and computer games per week), region, an indicator for self-reported heights and weights where necessary. Additional race/ethnicity information was controlled for in the non-EA subpopulations: oversampling of highly educated African Americans (AA stratum only), Hispanic subpopulation ancestry, as well as an indicator for foreign born (HA stratum only). Separate random effects allowed for individual, family and school with no sample weighting. Models run separately for each SNP, by high and low MVPA and race/ethnicity. P values corrected for multiple testing are α equal to 0.05/number of SNPs tested (0.0012 in EA and 0.0014 in HA).
2 Likelihood ratio tests were used to assess statistical interaction between the main effects (no interaction term) model and the interaction model, separately for each SNP by race/ethnicity.
3 High MVPA: 5 or more bouts per week of MVPA, low MVPA: less than 5 bouts per week of MVPA