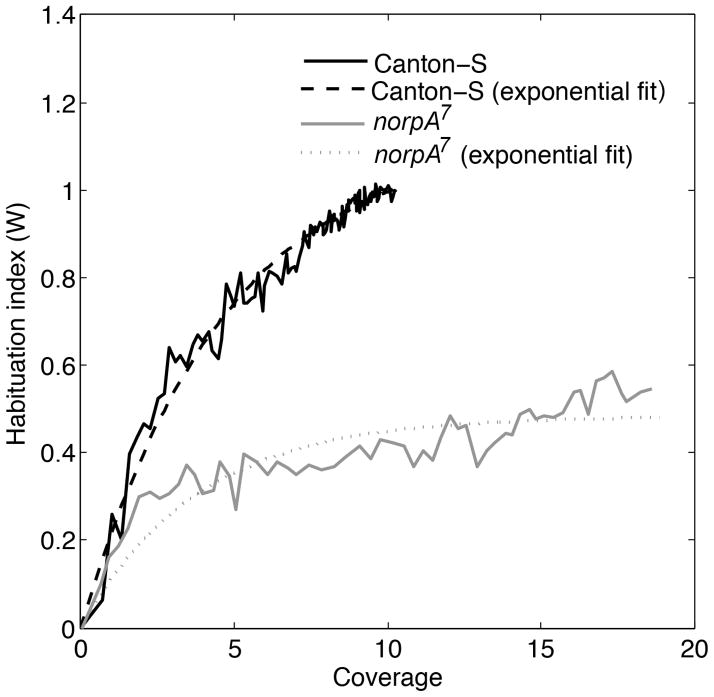
Figure 10. The habituation index discriminates between wild type and non-habituating blind flies.
This figure shows the habituation indices of Canton-S and norpA7 blind flies. As coverage increases the habituation index of the Canton-S flies increases, while the blind flies fails to do so. The habituation index of the blind flies increases to a value of 0.5 when coverage increases to a value of 18 approximately. While in Canton-S flies, the habituation index reaches the value of 1 when coverage attains a value of 11 approximately. This indicates that the blind flies require a significantly higher amount of exploration than Canton-S flies to habituate the arena.