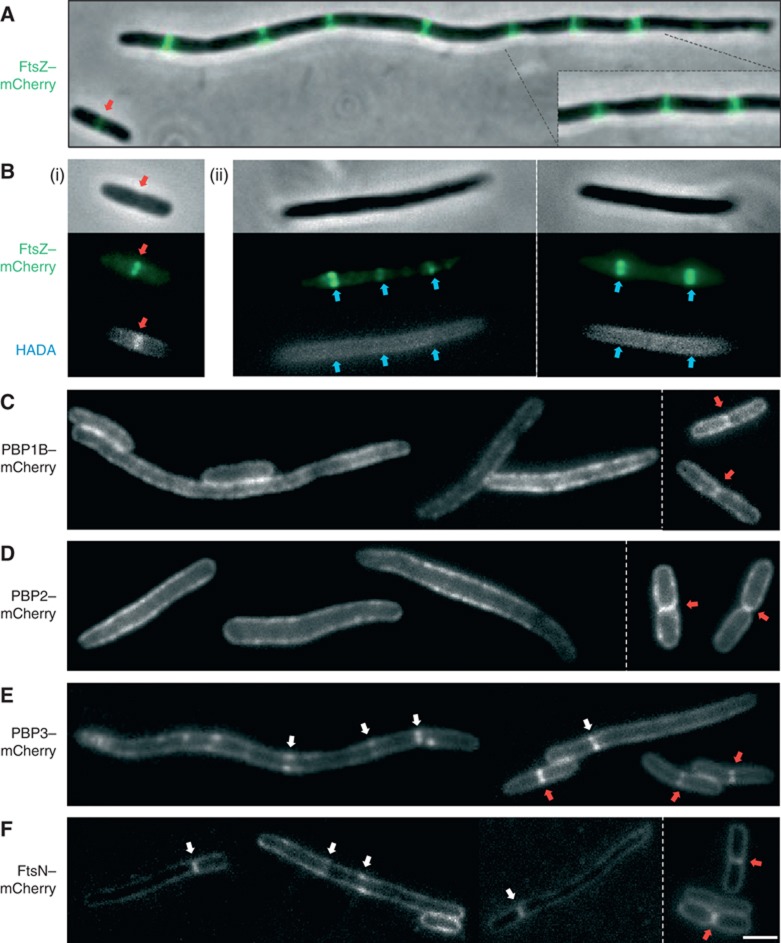
Figure 5.
PBPs are mislocalised and septal PG synthesis is inhibited in MreBD285A-expressing cells. MC1000 cells elongated by expressing MreBD285A from pAKF129 (PBAD::mreBD285ACD) containing a second plasmid expressing GFP-tagged division and elongation factors: (A, B) FtsZ–mCherry (pAKF133, PBAD::ftsZ–mCherry), (C) PBP1B–mCherry (pAKF145, Plac::mrcB–mCherry), (D) PBP2–mCherry (pAKF146, Plac::mrdA–mCherry), (E) PBP3–mCherry (pAKF147, Plac::ftsI–mCherry) and (F) FtsN–mCherry (pAKF150, Plac::mCherry-ftsN). In most cases cells were grown in M9 media for 5 h at 30°C with 0.000,05% arabinose. For expression from pAKF146, cells were grown in M9 glucose with 0.1% arabinose inducer. Empty vector and MreB overexpression control images are shown in Supplementary Figure S7; contrasting elongated cells treated with PBP3-sepcific inhibitors are shown in Supplementary Figure S8. Elongated cells contain multiple evenly spaced Z rings (A). Fixed HADA fluorescent D-aa-labelled cells (B). MC1000 pAKF133 cells containing empty pBAD24 vector (i) or elongated through MreBD285ACD expression from pAKF129 (ii) were incubated with 1 mM HADA for 30 s, cells were fixed using 70% ethanol and washed in PBS before microscopy. Note HADA incorporation at mature Z rings in (i—red arrows) are absent from elongated MreBD285A cells (ii—blue arrows), see Supplementary Figure S6C for FtsI inhibitor controls. Note FtsZ, PBP1B, PBP2, PBP3 and FtsN are all recruited to the septum during normal cell division—red arrows (Supplementary Figure S7). In MreBD285A elongated cells, PBP3 and FtsN are recruited to inhibit septa (E, F—white arrows), whereas PBP1B and PBP2 are not (D, E). The behaviours of tagged PBP–mCherry fusions are shown in Supplementary Figure S11. Images are representative of at least four independent repeats. Scale bar=2 μm.