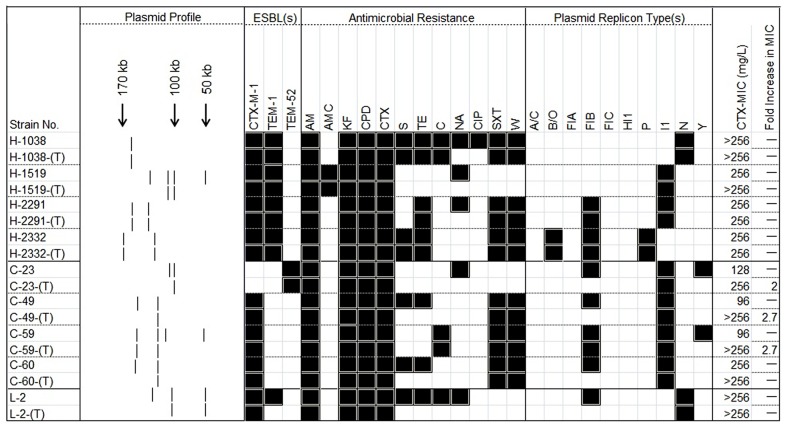
FIGURE 2.
A heat-map showing the comparison of ESBL-positive E. coli donors and the resultant transconjugants, characterized on the basis of their plasmid profiles; ESBL-markers identified by PCR; antimicrobial resistance profile; and plasmid replicon type(s). The MIC for cefotaxime in each pairwise combination is also shown along with the fold increase in this value. (T) in the first column typifies the transconjugant. Black and white squares denote the presence and absence, respectively of a particular feature. The symbol “–” signifies no fold-change in the MIC for the transconjugant. Antimicrobial compounds are abbreviated as follows: AM, ampicillin; AMC, amoxicillin–clavulanic acid; C, chloramphenicol; CPD, cefpodoxime; CIP, ciprofloxacin; CTX, cefotaxime; KF, cephalothin; NA, nalidixic acid; S, streptomycin; SXT, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole; TE, tetracycline; W, trimethoprim.