Figure 1.
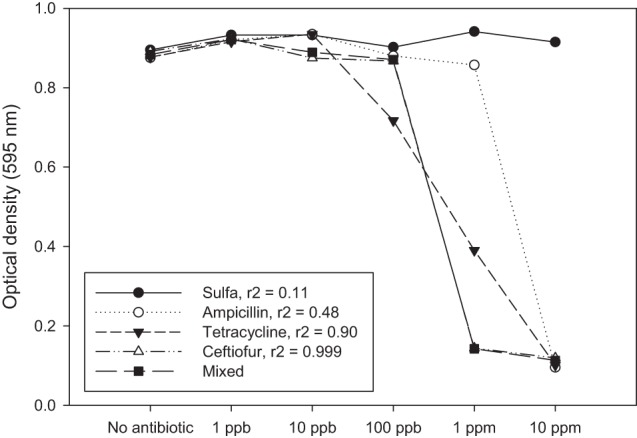
Antibiotic residues only affect bacteria from a fitness standpoint when the concentration of residue approaches a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). MIC values are typically > 1 ppm, whereas most environmental residue reported in the literature are found at ppb or ppt. These might be significant if there is an additive or synergistic effect attributed to exposure to multiple low-dose antibiotic residues. In this example, single antibiotics and a mixture of four antibiotics at the same concentration were tested against a sensitive strain of E. coli (K-12). The response to the mixture is most closely associated with ceftiofur (r2 = 0.999). If there was an additive or synergistic effect on fitness we would expect to see the mixed antibiotic (solid square) as having the lowest optical density at 100 ppb, which is not the case in this experiment. Each data point represents the optical density after 24 h growth in LB as measured using a Bioscreen plate reader. Average for three independent replicates is shown.
