Abstract
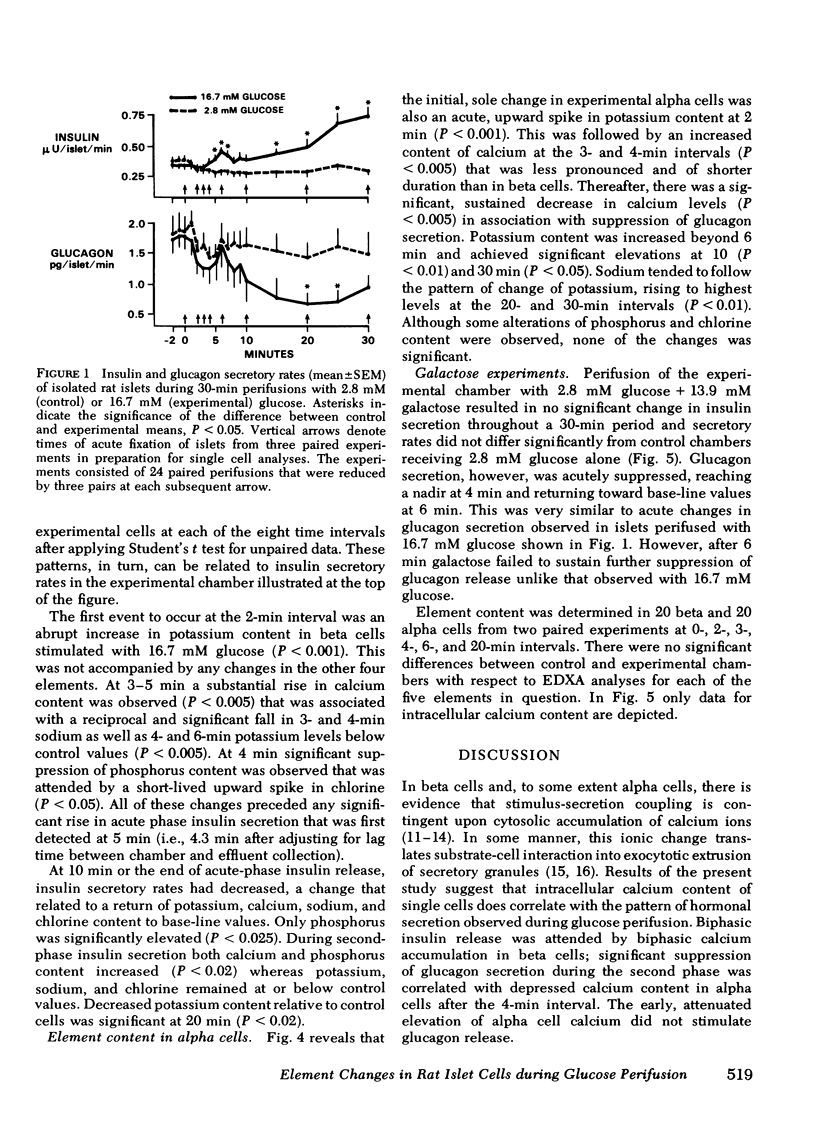
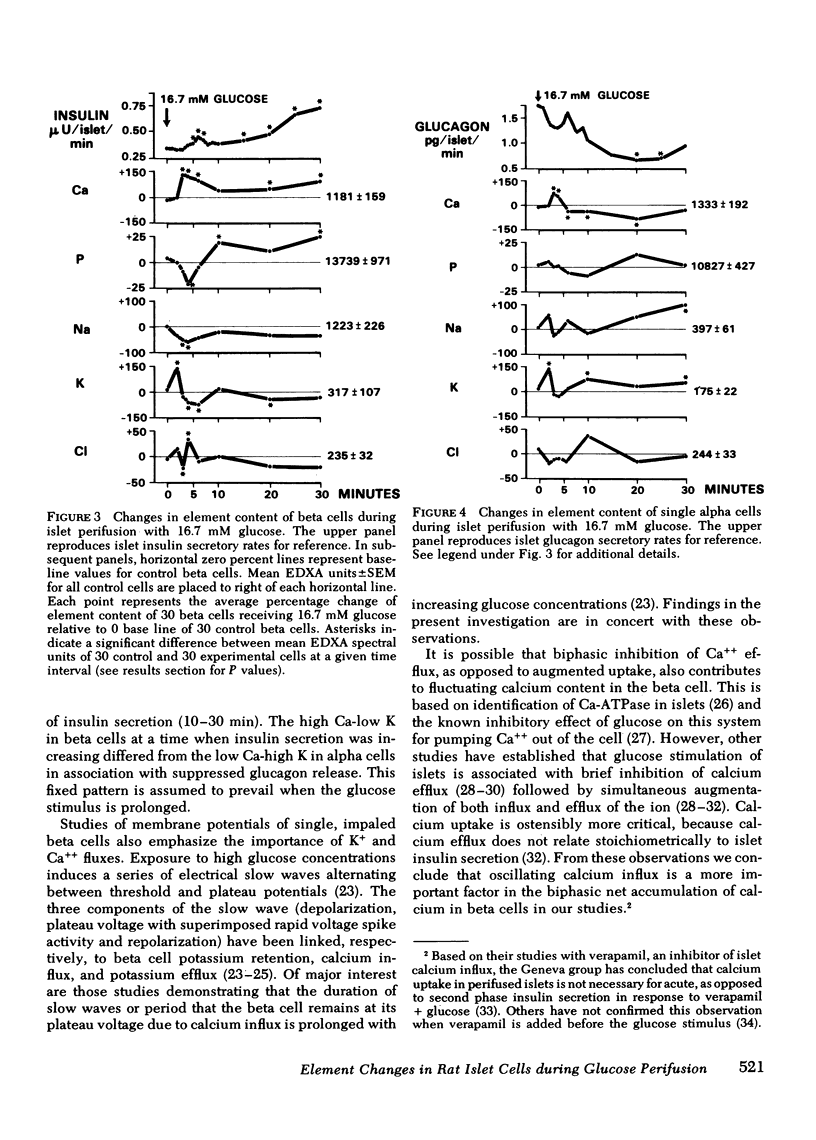
To study the relationship between islet hormonal secretion and intracellular content of five elements, a rat islet perifusion technique was used in 24 paired experiments. Control and experimental chambers each containing 100 islets, received 2.8 and 16.7 mM D-glucose, respectively. Effluent was collected frequently for hormone measurements. At eight different time intervals form 0--30 min islets were fixed and prepared for scanning electron microscopy. Over 900 unobscured alpha and beta cells were selected by size and shape criteria. Energy dispersive x-ray analysis was applied to each single cell to determine relative content of calcium (Ca), potassium (K), sodium (Na), chlorine (Cl), and phosphorus (P). Experimental chambers exhibited typical acute (0--9 min) and second phase (10--30 min) insulin secretion in association with suppression of glucagon release after 10 min. At 2 min an abrupt upward K spike in both alpha and beta cells was followed at 3--4 min with a 1.5- to 2-fold rise of Ca and a reciprocal decrease in K, Na, Cl, and P. From 3 to 30 min biphasic insulin secretion. Reduced alpha cell calcium after 6 min preceded suppression of glucagon secretion. After 2 min K related inversely to Ca content in both alpha and beta cells. These results could not be reproduced when D-galactose was substituted for D-glucose. We conclude that sequential changes of Ca content that are reciprocally related to K are predictive of beta cell insulin release and suppression of alpha cell glucagon secretion.
Full text
PDF

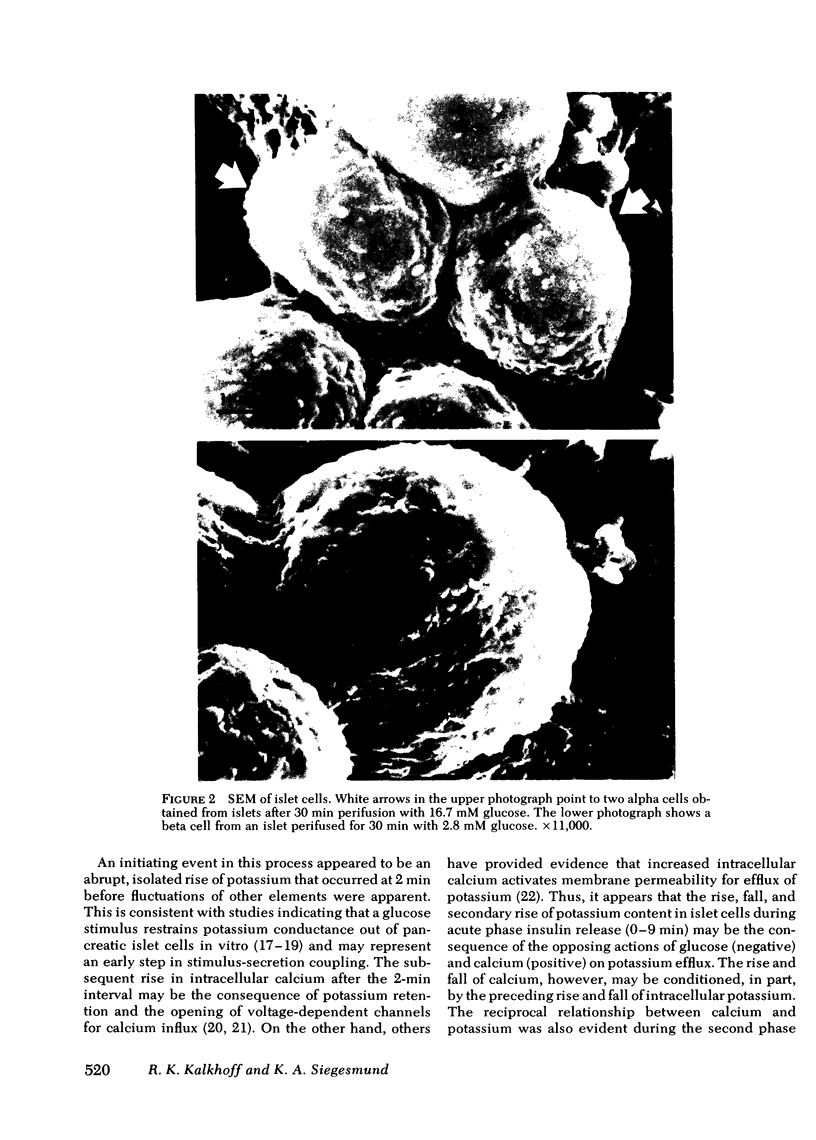


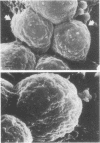
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashby J. P., Speake R. N. Insulin and glucagon secretion from isolated islets of Langerhans. The effects of calcium ionophores. Biochem J. 1975 Jul;150(1):89–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berglund O., Sehlin J. Defective regulation of Cl- permeability in islets of diabetic mice [C57BL/KsJ(db/db)]. Diabetes. 1980 Feb;29(2):151–155. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschero A. C., Kawazu S., Duncan G., Malaisse W. J. Effect of glucose on K+ handling by pancreatic islets. FEBS Lett. 1977 Nov 1;83(1):151–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80662-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschero A. C., Malaisse W. J. Effect of glucose on 22Na+ efflux in pancreatic islets. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1978 Aug;86(3):479–485. doi: 10.3109/13813457809055918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowiecki L., Freinkel N. Relationship between efflux of ionic calcium and phosphorus during excitation of pancreatic islets with glucose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 4;436(1):190–198. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90230-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles M. A., Lawecki J., Pictet R., Grodsky G. M. Insulin secretion. Interrelationships of glucose, cyclic adenosine 3:5-monophosphate, and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6134–6140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K. Electrical activity in pancreatic islet cells: effect of ions. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):265–275. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devis G., Somers G., Malaisse W. J. Stimulation of insulin release by calcium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 17;67(2):525–529. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90843-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formby B., Capito K., Egeberg J., Hedeskov C. J. Ca-activated ATPase activity in subcellular fractions of mouse pancreatic islets. Am J Physiol. 1976 Feb;230(2):441–448. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.2.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel B. J., Imagawa W. T., O'Connor M. D., Lundquist I., Kromhout J. A., Fanska R. E., Grodsky G. M. Glucose-stimulated 45Calcium efflux from isolated rat pancreatic islets. J Clin Invest. 1978 Sep;62(3):525–531. doi: 10.1172/JCI109156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freinkel N., Pedley K. C., Wooding P., Dawson R. M. Localization of inorganic phosphate in the pancreatic B cell and its loss on glucose stimulation. Science. 1978 Sep 22;201(4361):1124–1126. doi: 10.1126/science.356269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freinkel N., Younsi C. E., Bonnar J., Dawson R. M. Rapid transient efflux of phosphate ions from pancreatic islets as an early action of insulin secretagogues. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1179–1189. doi: 10.1172/JCI107861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M., Bennett L. L. Cation requirements for insulin secretion in the isolated perfused pancreas. Diabetes. 1966 Dec;15(12):910–913. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.12.910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B. Stimulation of insulin release after raising extracellular calcium. FEBS Lett. 1976 Mar 15;63(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. D-glucose inhibits potassium efflux from pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1978 Jan 19;271(5642):271–273. doi: 10.1038/271271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Opposite effects of intracellular Ca2+ and glucose on K+ permeability of pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1979 Jul 5;280(5717):66–68. doi: 10.1038/280066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalkhoff R. K., Kim H. J. Effects of pregnancy on insulin and glucagon secretion by perifused rat pancreatic islets. Endocrinology. 1978 Feb;102(2):623–631. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-2-623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawazu S., Boschero A. C., Delcroix C., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XXVIII. Effect of glucose on Na+ fluxes in isolated islets. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Jul 18;375(2):197–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00584244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi M., Wollheim C. B., Cuendet G. S., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W. Studies on the dual effects of glucose on 45Ca++ efflux from isolated rat islets. Endocrinology. 1978 May;102(5):1339–1349. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-5-1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E. Endocrine secretory mechanisms. A review. Am J Pathol. 1975 Apr;79(1):170–188. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967 Jan;16(1):35–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Walker M. M., Fink C. J. Perifusion of isolated rat islets in vitro. Participation of the microtubular system in the biphasic release of insulin. Diabetes. 1972 Oct;21(10):987–998. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.10.987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechene C. Electron probe microanalysis of biological soft tissues: principle and technique. Fed Proc. 1980 Sep;39(11):2871–2880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclercq-Meyer V., Marchand J., Malaisse W. J. The effect of calcium and magnesium on glucagon secretion. Endocrinology. 1973 Dec;93(6):1360–1370. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-6-1360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin S. R., Kasson B. G., Driessen J. F. Adenosine triphosphatases of rat pancreatic islets: comparison with those of rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1978 Sep;62(3):692–701. doi: 10.1172/JCI109177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse-Lagae F., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. 3. Uptake of 45 calcium by isolated islets of Langerhans. Endocrinology. 1971 Jan;88(1):72–80. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-1-72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Brisson G. R., Baird L. E. Stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. X. Effect of glucose on 45 Ca efflux from perifused islets. Am J Physiol. 1973 Feb;224(2):389–394. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.2.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A. N. Calcium pumps: introduction. Fed Proc. 1980 May 15;39(7):2401–2402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P., Preissler M. Glucose-induced changes of the membrane potential of pancreatic B-cells: their significance for the regulation of insulin release. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1979;119:97–107. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9110-8_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P., Schmelz H. Membrane potential of beta-cells in pancreatic islets. Pflugers Arch. 1974;351(3):195–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00586918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naber S. P., McDaniel M. L., Lacy P. E. The effect of glucose on the acute uptake and efflux of calcium-45 in isolated rat islets. Endocrinology. 1977 Sep;101(3):686–693. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-3-686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Malaisse W. Hypothesis: single and chain release of insulin secretory granules is related to anionic transport at exocytotic sites. Diabetes. 1980 Nov;29(11):943–944. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.11.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace C. S. Activation of Na channels in islet cells: metabolic and secretory effects. Am J Physiol. 1979 Aug;237(2):E130–E135. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.2.E130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce M., Freinkel N., Dawson R. M., Asplund K., Bukowiecki L. 32P-labeling patterns in rat pancreatic islets: tissue source of the radiophosphate released after glucose stimulation. Endocrinology. 1978 Sep;103(3):971–977. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-3-971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribalet B., Beigelman P. M. Cyclic variation of K+ conductance in pancreatic beta-cells: Ca2+ and voltage dependence. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):C137–C146. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1979.237.3.C137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocha D. M., Faloona G. R., Unger R. H. Glucagon-stimulating activity of 20 amino acids in dogs. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2346–2351. doi: 10.1172/JCI107046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehlin J., Taljedal I. B. Glucose-induced decrease in Rb+ permeability in pancreatic beta cells. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):635–636. doi: 10.1038/253635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Sodium uptake by microdissected pancreatic islets: effects of ouabain and chloromercuribenzene-p-sulphonic acid. FEBS Lett. 1974 Feb 15;39(2):209–213. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel E. G., Wollheim C. B., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W. Evidence for the involvement of Na/Ca exchange in glucose-induced insulin release from rat pancreatic islets. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):996–1003. doi: 10.1172/JCI109969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen E., Somers G., Devis G., Ravazzola M., Malaisse-Lagae F., Orci L., Malaisse W. J. Dynamics of insulin release and microtubular-microfilamentous system. VII. Do microfilaments provide the motive force for the translocation and extrusion of beta granules? Diabetes. 1975 Oct;24(10):892–901. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.10.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Kikuchi M., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W. The roles of intracellular and extracellular Ca++ in glucose-stimulated biphasic insulin release by rat islets. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):451–458. doi: 10.1172/JCI109146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimny M. L., Blackard W. G. The surface structure of isolated pancreatic islet cells. Cell Tissue Res. 1975 Dec 18;164(4):467–471. doi: 10.1007/BF00219938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]