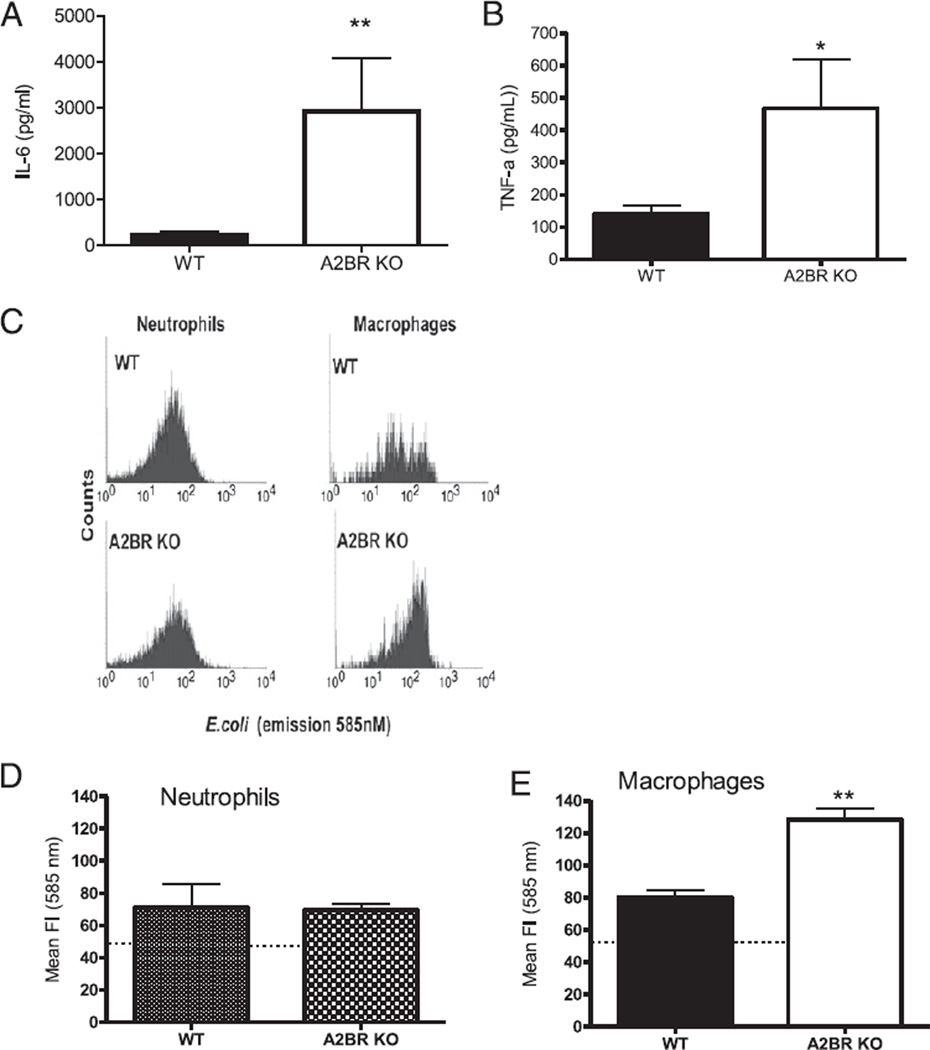
FIGURE 4.
A2BR deficiency enhances macrophage function. Peritoneal cells used in these experiments were analyzed from either A2BR KO or WT mice subjected to CLP and harvested 24 h later. LPS stimulation enhanced cytokine release from macrophages isolated from septic A2BR-deficient mice. Isolated peritoneal macrophages from septic mice were stimulated ex vivo with 100 ng/ml LPS for 24 h. Supernatants were measured for IL-6 (A) and TNF-α (B) by ELISA. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Gated neutrophil and macrophage populations were identified as Gr-1highF4/80negative and Gr-1lowF4/80positive to discriminate between neutrophil and macrophage bacteria phagocytosis activity, respectively, from other cell types. C, Histogram of gated neutrophil and macrophage populations showing the phagocytic/endocytic capacity of phagocytes from septic WT and A2BR KO mice preincubated with the pH-sensitive fluorogenic E. coli. E. coli present inside the phagolysosome are highly fluorescent relative to nonendocytosed E. coli. Quantitative analysis of the phagocytic activity for neutrophils (D) (Gr-1highF4/80negative) and macrophages (E) (Gr-1lowF4/80positive) from septic WT and A2BR KO mice. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared with WT CLP mice.