Fig. 1.
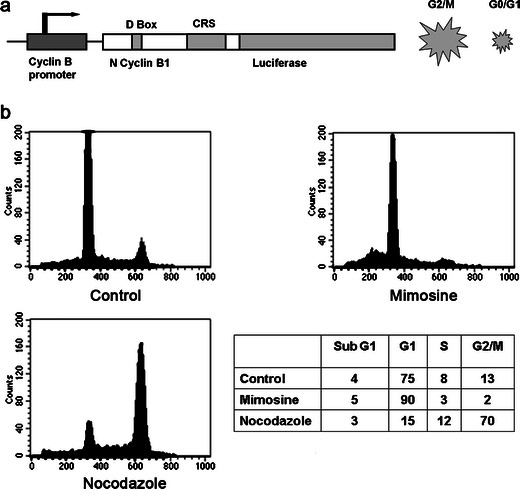
The mechanism of the fusion protein of cyclin B-Luc, regulated by the cyclin B promoter. a A schematic drawing of the mitotic reporter. A fusion protein of the N terminus of cyclin B fused to luciferase is driven by a cyclin B promoter. The N-terminal domain of cyclin B1 contains a conserved nine-amino-acid motif (RTALGDIGN) called the D-box that is necessary for cyclin B1 ubiquitination and subsequent degradation. The CRS region is responsible for nuclear/cytoplasmic shuttling of cyclin B. In the G2/M phase of the cell cycle, the reporter is stabilized and is degraded during the G0/G1 phase. b Polyclonal HeLa cells stably transfected with pGL3-cyclin B-Luc (HeLa-cyclin B-Luc) were synchronized by growth in media containing 0.2 mM mimosine or 500 nM nocodazole for 18 h. Mimosine arrested 90 % of cells in the late G1 phase, while 500 nM nocodazole arrested 70 % of cells in G2/M phase.
