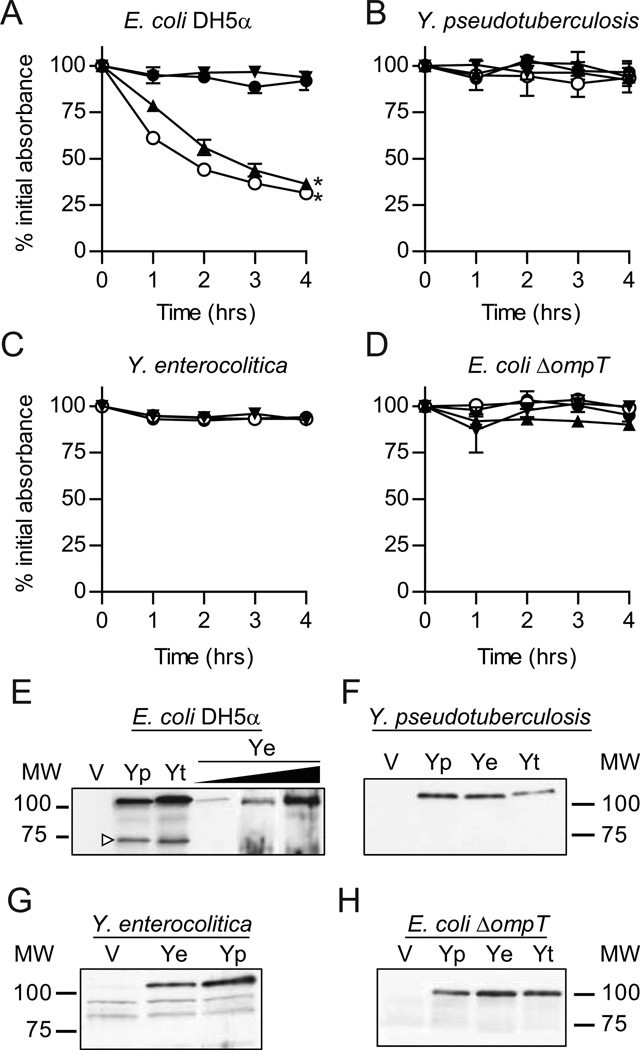
Figure 1. Analysis of YapE-mediated aggregation.
For settling assays, YapE otholog expression was induced for 2 hrs and then samples were harvest from static cultures at a specific depth at 1 hr intervals. The absorbance (OD600) of these samples were determined and compared to the OD600 at T=0. (A) E. coli, (B) Y. pseudotuberculosis, (C) Y. enterocolitica, and (D) E. coli ΔompT. ● = Vector only (pLP-PROTet- 6xHN); ○ = Y. pestis YapE (pMBL295); ▲ = Y. pseudotuberculosis YapE (pMBL299); ▼ = Y. enterocolitica YapE (pMBL291). Three independent biological replicates were performed for each bacterial strain and each assay was repeated three times (n=9). Each symbol represents the mean percent initial absorbance ± the standard deviation; *=P≤0.0005. At 4 hrs, 1 OD600 equivalents of total bacterial proteins were isolated from one representative sample and YapE processing was determined by Western blot with anti-YapE serum. (E) E. coli, (F) Y. pseudotuberculosis, (G) Y. enterocolitica, (H) E. coli ΔompT. V = vector; Yp = Y. pestis YapE; Yt = Y. pseudotuberculosis YapE; Ye = Y. enterocolitica YapE. White arrowhead indicates processed YapE. Black triangle represents addition of increasing concentrations of anhydrous tetracycline to demonstrate that increasing the levels of expression does not result in cleavage of Ye.