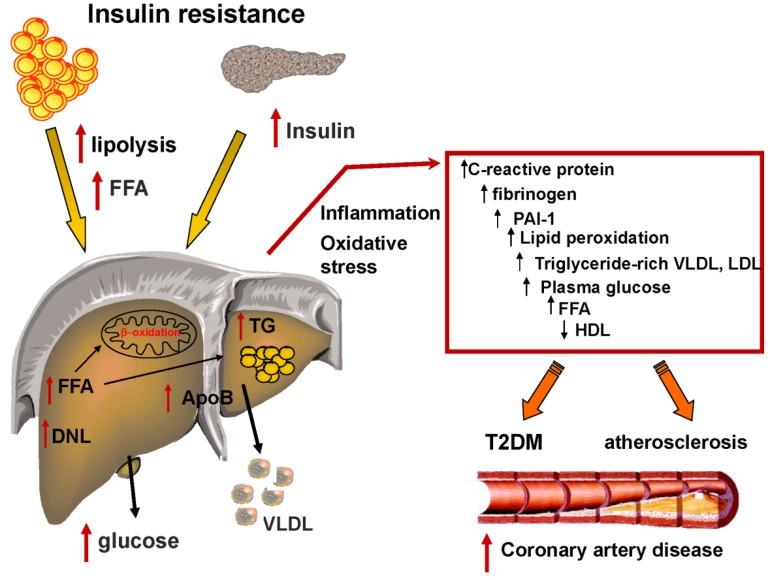
Figure 4.
Link between insulin resistance and metabolic dyslipidemia. Insulin resistance is associated with an increase of free fatty acids (FFAs) flux that contributes to increased TG production that, in turn, stimulate assembly and secretion of VLDL in hepatocytes. Fat accumulation in the liver is associated with oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation. Furthermore NAFLD subjects have increased secretion of inflammatory markers, plasma glucose and a decrease in HDL concentration. The consequence of this physiological dysfunction is increased risk for the development of diabetes and atherosclerosis and increased risk for coronary artery disease.