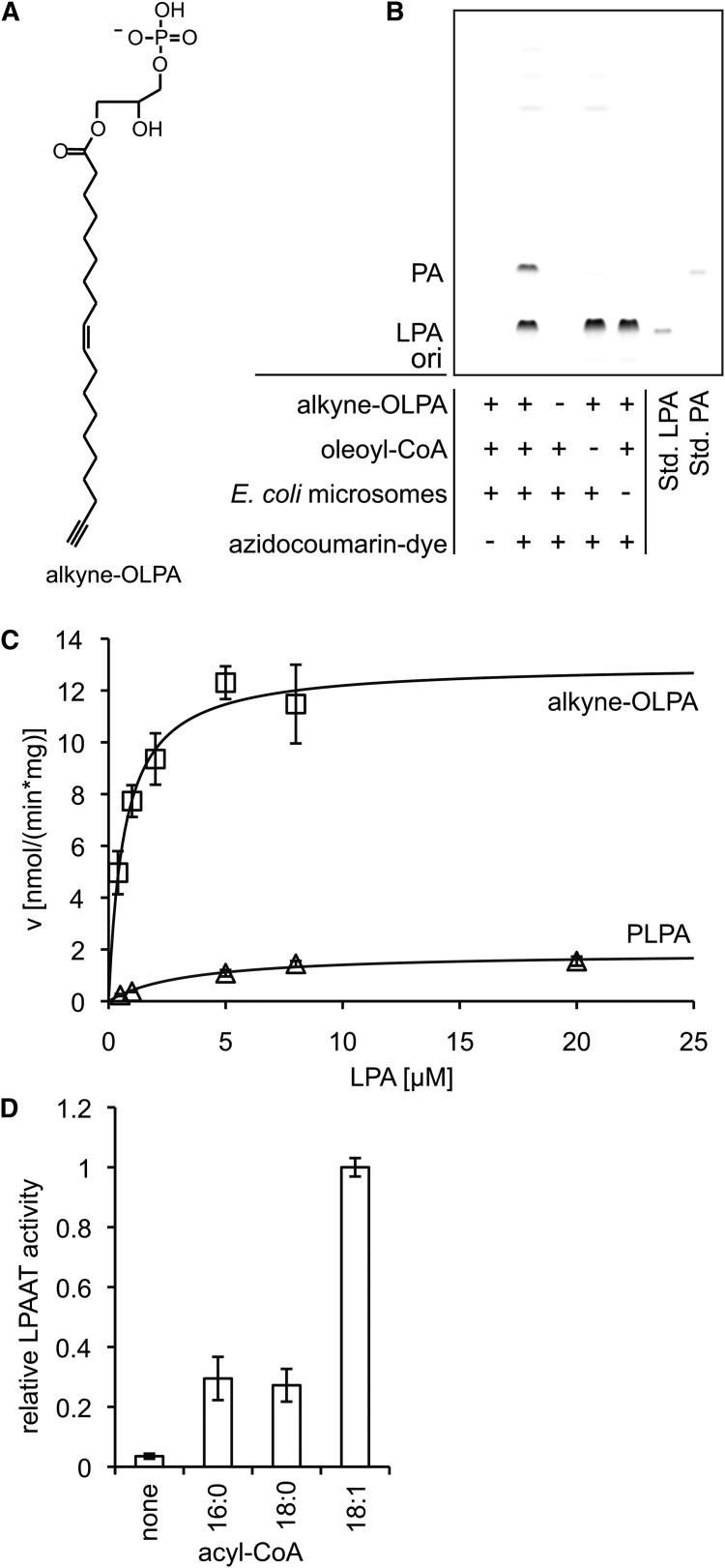
Fig. 2.
LPAAT assay using alkyne-OLPA or alkyne-oleoyl-CoA. Alkyne-OLPA [structure in panel (A)] or alkyne-oleoyl-CoA were used as labeled substrates in a LPAAT assay with E. coli microsomes. B: Fluorescent TLC image of the LPAAT assay with alkyne-OLPA. Product PA was identified using comigrating synthetic alkyne-OOPA. For assay details, see Materials and Methods. “ori” depicts the origin of the TLC. C: Michaelis-Menten kinetics measured for alkyne-OLPA (squares) and PLPA (triangles). Oleoyl-CoA was the acyl chain donor for alkyne-OLPA, whereas alkyne-oleoyl-CoA was used to detect enzymatic activity toward PLPA. Line graphs show the reaction rate (v) calculated with the Michaelis-Menten equation using the values for Vmax and Km obtained by nonlinear regression fitting. Data are mean ± SD of triplicate determinations. D: Acyl-CoA specificity of the E. coli LPAAT using alkyne-OLPA. The monounsaturated 18:1-CoA is favored over the saturated acyl-CoAs (16:0 and 18:0).