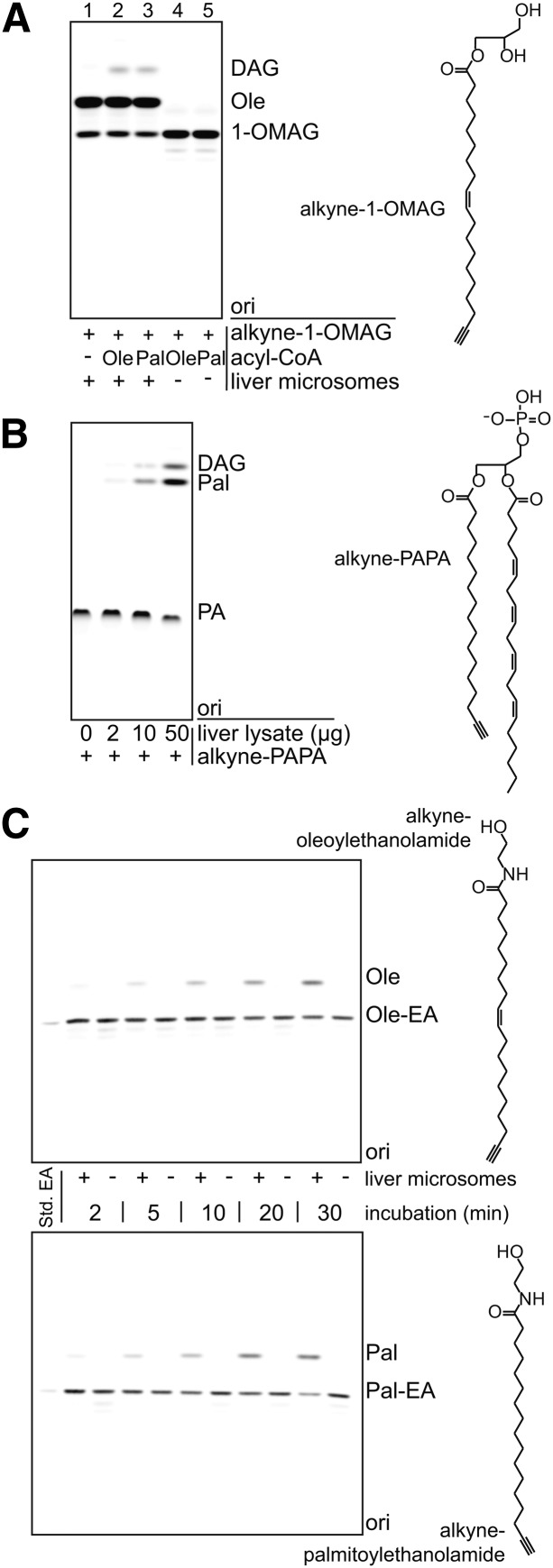
Fig. 5.
Application of alkyne lipids in assays for other lipid-modifying enzymes. Four different alkyne lipids were incubated with mouse liver microsomes or lysate (C57BL/6 wild-type) to test their applicability as substrates in enzymatic assays. A: Alkyne-1-OMAG deacylation and acylation. Alkyne-1-OMAG was incubated with liver microsomes in the absence (−) or presence (+) of acyl-CoAs as indicated. The data indicate both hydrolysis to oleate (Ole) in the presence of liver microsomes and acylation to DAG if an acyl-CoA is present. B: Alkyne-PAPA deacylation and dephosphorylation. Alkyne-PAPA was incubated with different amounts of liver lysate as indicated. We observed both release of alkyne-palmitate (Pal) and dephosphorylation to DAG. C: Time course of the hydrolysis of fatty acid ethanolamides by liver microsomes. Alkyne-oleoylethanolamide (Ole-EA) and alkyne-palmitoylethanolamide (Pal-EA) were hydrolyzed upon incubation with the microsomes, but not in their absence, to give the alkyne-labeled fatty acids. A–C: Products were identified using comigrating synthetic standards (Std. EA). “ori” depicts the origin of the TLC. For assay details, see Materials and Methods.