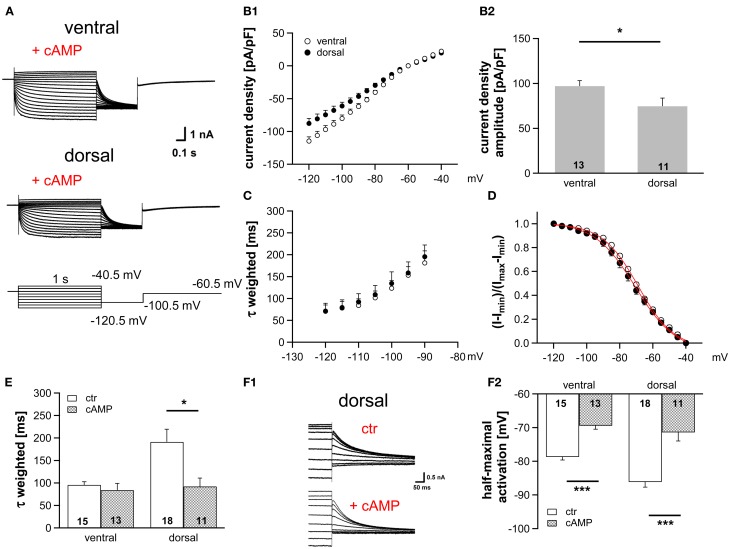
Figure 2.
Modulation of Ih by cAMP differs along the dorsoventral axis. (A) Current responses to depolarizing and hyperpolarizing voltage steps were recorded from MSO neurons in the ventral and dorsal part of the MSO with 25 μM cAMP in the pipette solution. (B) Ih density gradient persists in the presence of cAMP as illustrated by the current-voltage relationships for ventral (n = 13) and dorsal (n = 11) neurons (B1) and their Ih density amplitudes for a −110.5 mV voltage step (B2). (C) The weighted activation time constants and (D), the voltage dependence of Ih activation overlap in the presence of cAMP. Comparison of (E) the weighted activation time constants and (F) the half-maximal activation voltages in the absence and presence of 25 μM cAMP reveals that dorsal neurons are more sensitive to cAMP than ventral neurons (F2). (F1) In the upper panel, tail currents were elicited using standard pipette solution. In the lower panel, a different, dorsal neuron is illustrated using standard pipette solution supplemented with 25 μM cAMP. Black symbols: dorsal neurons; white symbols: ventral neurons. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, two-tailed, unpaired t-test.