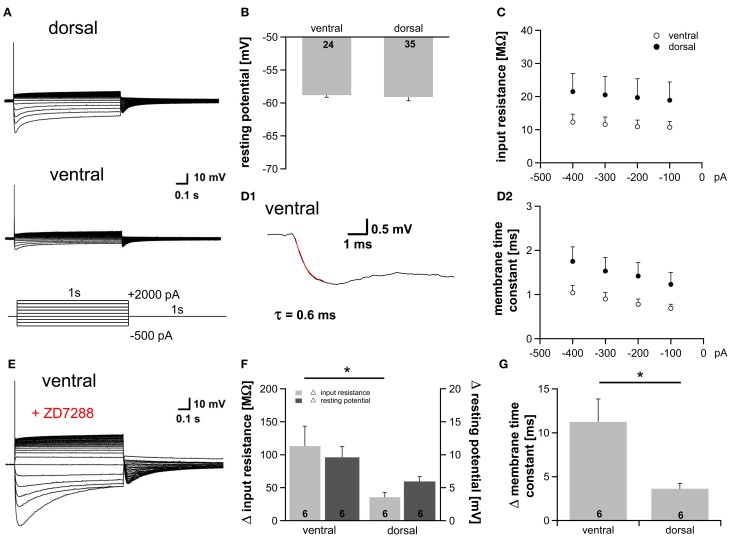
Figure 3.
Gradient of Ih affects membrane properties. (A) MSO neurons in the dorsal and in the ventral part of the MSO fire a single spike at the onset of depolarizing current injections and exhibit a voltage sag during hyperpolarizing current steps. (B) Resting membrane potential, (C) peak input resistance, and (D) membrane time constant are not significantly different between ventral (n = 18) and dorsal (n = 25) neurons (D2). The membrane time constant was fitted by a single-exponential function as shown in (D1). (E) Blocking Ih with 20 μM ZD7288, a specific Ih blocker, hyperpolarizes the cell, increases the input resistance and the membrane time constant. Same ventral neuron as in (A) but after treatment with 20 μM ZD7288. The differences in (F) the input resistance (light-gray bars), the resting potential (dark-gray bars) and (G) the membrane time constant before and after application of 20 μM ZD7288 varies between ventral and dorsal neurons. The effects are more pronounced in ventral neurons. Black symbols: dorsal neurons; white symbols: ventral neurons. *P < 0.05, two-tailed unpaired t-test.