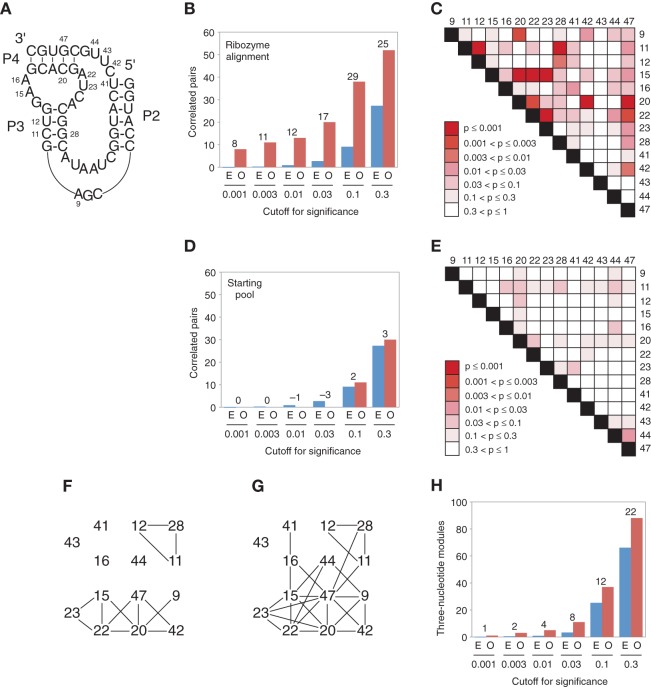
FIGURE 4.
Network of correlated positions in the kinase ribozyme. (A) Secondary structure of the minimized catalytic core of the ribozyme. Positions that were variable in the synthetically shuffled pool are numbered. (B) Number of correlated pairs of positions in the ribozyme variants observed at the indicated cutoffs for significance of mutual information values (O, red bars). For comparison, the expected number of correlations in a randomly shuffled sequence alignment is also plotted (E, blue bars), with the number of correlated pairs observed in excess over those expected by chance indicated (numbers above bars). (C) Heat map showing the significance of mutual information correlations for each of the 91 pairs of analyzed positions in the ribozyme alignment. (D) Number of correlated pairs of positions in the starting pool observed at the indicated cutoffs for significance of mutual information values. Otherwise, as in panel B. (E) Heat map showing the significance of mutual information correlations for each of the 91 pairs of analyzed positions in an alignment of sequences from the starting pool. (F) Network of correlated positions among the 14 synthetically shuffled nucleotides in the minimized catalytic core of the ribozyme. Lines indicate 13 pairs of positions with mutual information values expected to occur no more than once in every 100 randomized control alignments (P ≤ 0.01). (G) Same as panel F, except lines indicate 26 pairs of positions with mutual information values expected to occur no more than once in every 20 randomized control alignments (P ≤ 0.05). (H) Number of 3-nt modules in the ribozyme network observed at the indicated cutoffs for significance of mutual information values (O, red bars). For comparison, the expected number of 3-nt modules in a randomly shuffled network with the same number of links is also plotted (E, blue bars), with the number of modules observed in excess over those expected by chance indicated (numbers above bars).