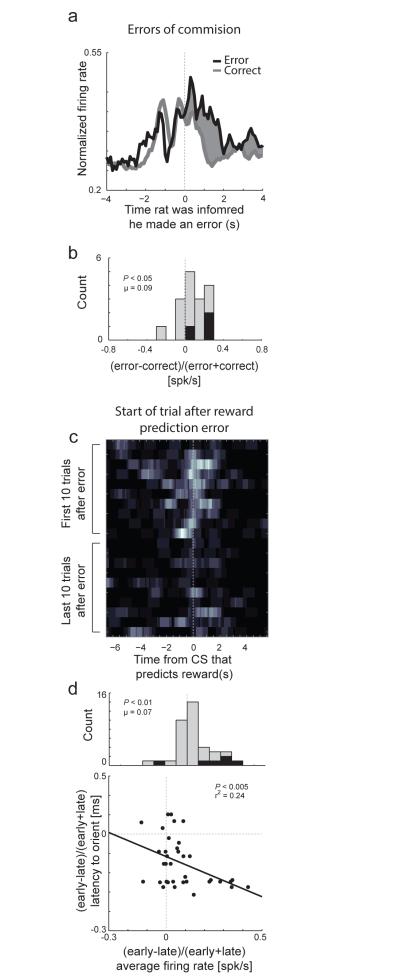
Figure 3.
Activity in ACC was high after errors of commission, errors in reward prediction, and was high at the beginning of trials that followed errors. a, Average activity of error related (1s following well entry) neurons upon errors of commission. b, Distribution reflecting the difference in activity between forced-choice errors and forced-choice correct trials ((error −correct) /(error + correct)). Black bars represent the number of neurons that showed a significant difference between these responses (t-test; p < 0.05). c, Heat plot shows the average firing of a single ACC neuron when reward contingences unexpectedly change (reward prediction error). d. Activity of ACC neurons fire more strongly after reward prediction errors and was correlated with attention. Correlation between latency to initiate behavioral trial and firing rate (x-axis) either early or late during learning ((early-late)/(early+late)). N = 4 rats. Modified from Bryden et al, 2011[143]