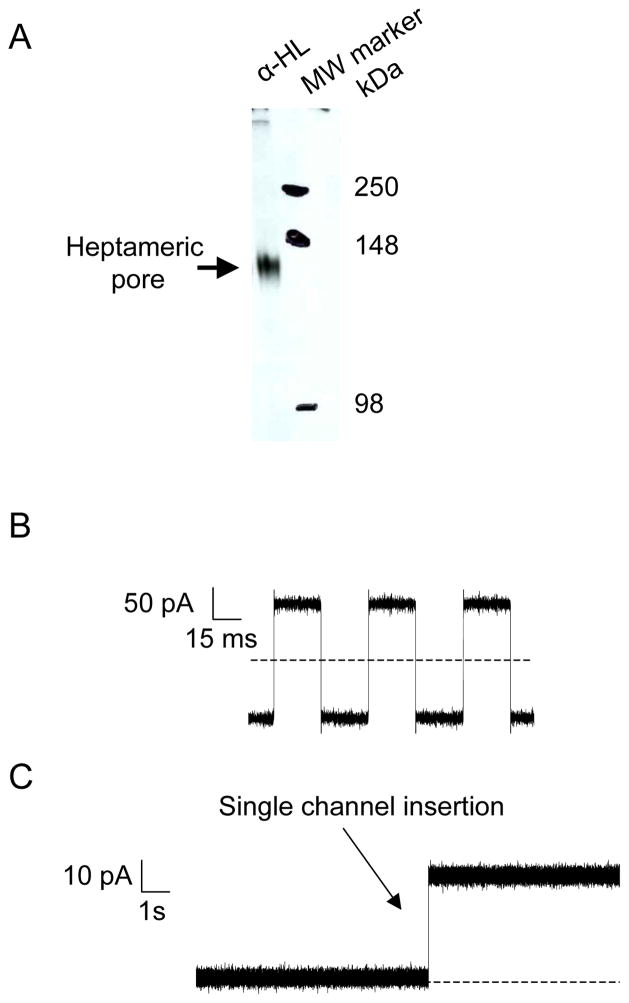
Fig. 3.
SDS-PAGE-purified αHL proteins form an aqueous channel in an artificial lipid bilayer. (A) Expression and assembly of the αHL protein pore. WT-αHL proteins were translated in IVTT reactions in the presence of red blood cell membranes. Proteins were separated on an 8% SDS-polyacrylamide gel. Molecular-weight markers are indicated on the right-hand side; (B) Application of external pulses with which the membrane capacitance of the bilayer can be measured; (C) Capture of the channel insertion during single-channel electrical recording. SDS-PAGE purified proteins were added to the cis chamber, stirred for few seconds and a single αHL protein pore was allowed to insert without further stirring. Single-channel recordings were carried out at room temperature in 1 M KCl, 10 mM potassium phosphate, pH 7.4 with an applied transmembrane potential of +40 mV. Dashed lines represent zero current in (B) and (C). The single-channel electrical traces were low-pass Bessel filtered at 2 kHz.