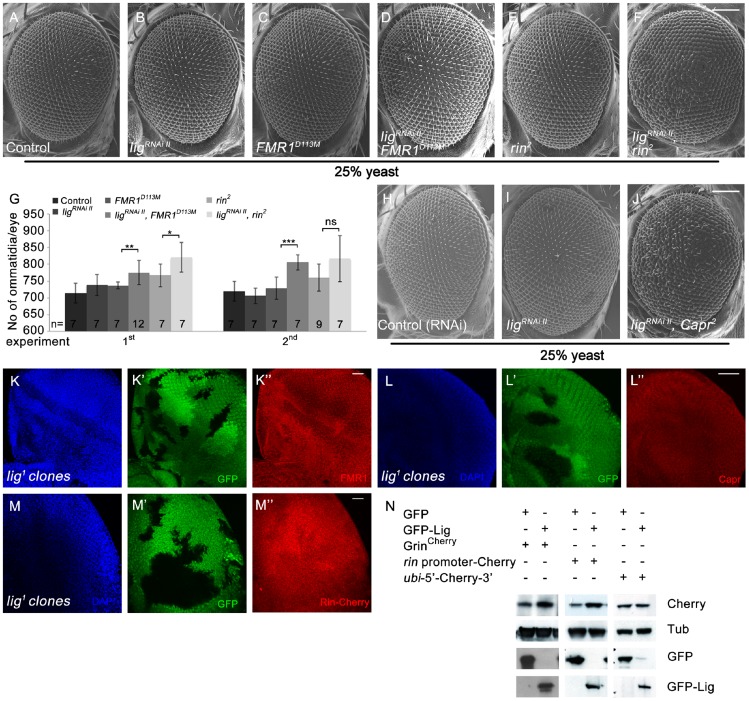
Figure 7. Lig cooperates with FMR1, Rin and Capr in growth control and regulates rin at the transcriptional level.
(A–G) Scanning electron micrographs of adult control (A), ligRNAi II (B), FMR1D113M (C), ligRNAi II FMR1D113M (D), rin2 (E), ligRNAi II rin2 (F) eyes generated by eyFLP Actin-Flp out-Gal4/FRT-mediated mitotic recombination from flies grown at 25% yeast content (A–F). Scale bar represents 100 µm. (G) Statistical analyses as described in Figure 1D: control (714±30 and 720±30), ligRNAi II expressing (738±32 and 706±23), FMR1D113M mutant (737±10 and 729±34), ligRNAi II expressing FMR1D113M mutant (775±36; p = 0.0051 and 806±23; p = 0.00046), rin2 mutant (767±34 and 760±40), ligRNAi II expressing rin2 mutant (821±45; p = 0.03 and 817±69; p = 0.082) eyes from flies raised on 25% yeast-containing food. (H–J) Scanning electron micrographs of adult control (H), ligRNAi II (I) and ligRNAi II Capr2 (J) eyes generated by eyFLP Actin-Flp out-Gal4/FRT Minute-mediated mitotic recombination from flies grown on 25% yeast-containing food. (K–M'') Negatively marked 72 h old lig1 mutant clones (induced with the hsFLP/FRT system) in eye imaginal discs of third instar larvae (K', L' and M'). FMR1 levels (visualized by immunostaining) remain unchanged (K''). Capr levels (visualized by immunostaining) are slightly increased in lig mutant clones (L''). Rin-Cherry levels expressed from the GrinCherry transgene are autonomously decreased in the lig1 mutant clones (M''). Imaginal discs are stained with DAPI (blue) to visualize the DNA. Scale bar represents 25 µm. (N) S2 cells transfected with GFP-Lig and GrinCherry have increased levels of Rin-Cherry in comparison to S2 cells overexpressing GFP and GrinCherry. S2 cells overexpressing GFP-Lig upregulate a transcriptional reporter consisting of the rin promoter followed by a Cherry coding sequence and the 3′ UTR of rin. Conversely, a translational reporter consisting of an ubi promoter followed by the 5′ UTR of rin, a Cherry protein coding sequence and the 3′ UTR of rin is not affected. Genotypes: (A) y w eyFLP, Act>CD2>Gal4/y w; FRT82 cl w+/FRT82 (B) y w eyFLP, Act>CD2>Gal4/y w; UAS-ligRNAi II [51D]/+; FRT82 cl w+/+ (C) y w eyFLP, Act>CD2>Gal4/y w; FRT82 cl w+/FRT82 FMR1D113M (D) y w eyFLP, Act>CD2>Gal4/y w; UAS-ligRNAi II [51D]/+; FRT82 cl w+/FRT82 FMR1D113M (E) y w eyFLP, Act>CD2>Gal4/y w; FRT82 cl w+/FRT82 rin2 (F) y w eyFLP, Act>CD2>Gal4/y w; UAS-ligRNAi II [51D]/+; FRT82 cl w+/FRT82 rin2 (H) y w eyFLP, Act>CD2>Gal4/y w; UAS-CG1315RNAi (control)/+; M(3)RpS174 FRT80/+ (I) y w eyFLP, Act>CD2>Gal4/y w; UAS-ligRNAi II [51D]/+; M(3)RpS174 FRT80/+ (J) y w eyFLP, Act>CD2>Gal4/y w; UAS-ligRNAi II [51D]/+; M(3)RpS174 FRT80/Capr2 FRT80 (K, L) y w hsFLP/y w; FRT42 ubiGFP/FRT42 lig1 (M) y w hsFLP/y w; FRT42 ubiGFP/FRT42 lig1; GrinCherry [86Fb]/+.