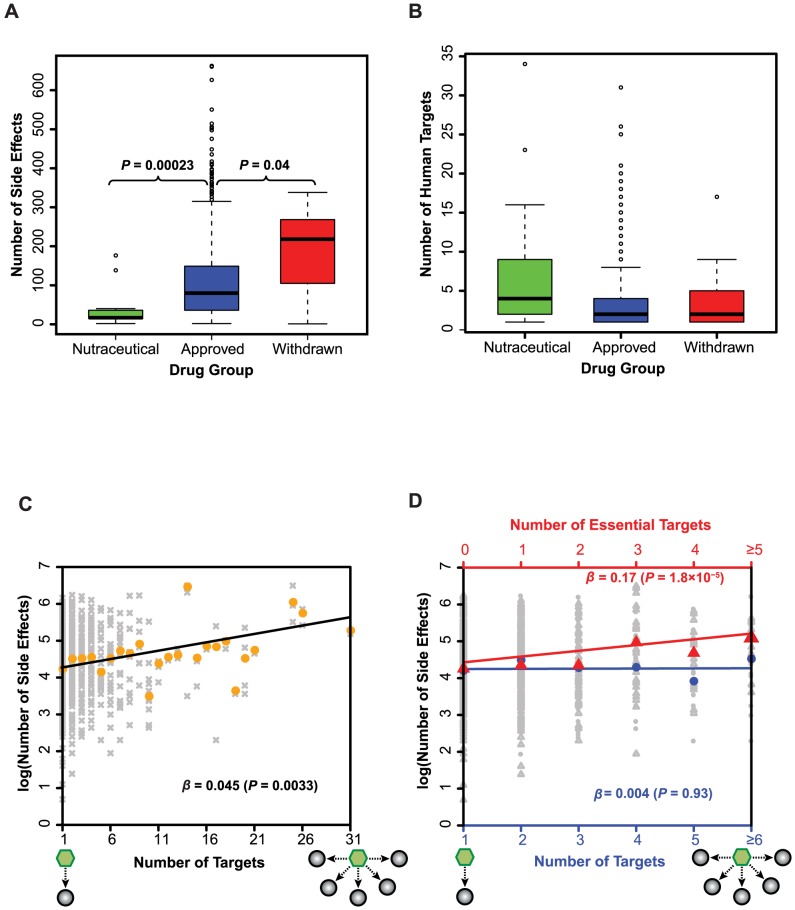
Figure 2. The number of side effects is positively correlated with the number of essential targets.
(A) The number of side effects and (B) the number of human targets are displayed for different groups of drugs. The Wilcoxon rank-sum tests were used to assess the differences in distributions of side effects and human targets among different drug groups. The number of drug side effects is positively correlated with (C) the number of total targets and (D) the number of essential targets (triangles). However, the analysis on drugs with no essential targets shows no correlation between drug side effects and targets (circles). The results in panels (C) and (D) are obtained from generalized linear regressions based on negative binomial distribution for side effects. In panels (C) and (D), gray symbols are raw data while the colored ones correspond to median counts of side effects. Schematics under the x-axes illustrate a drug (hexagon) binding to its target protein(s) (filled circles).