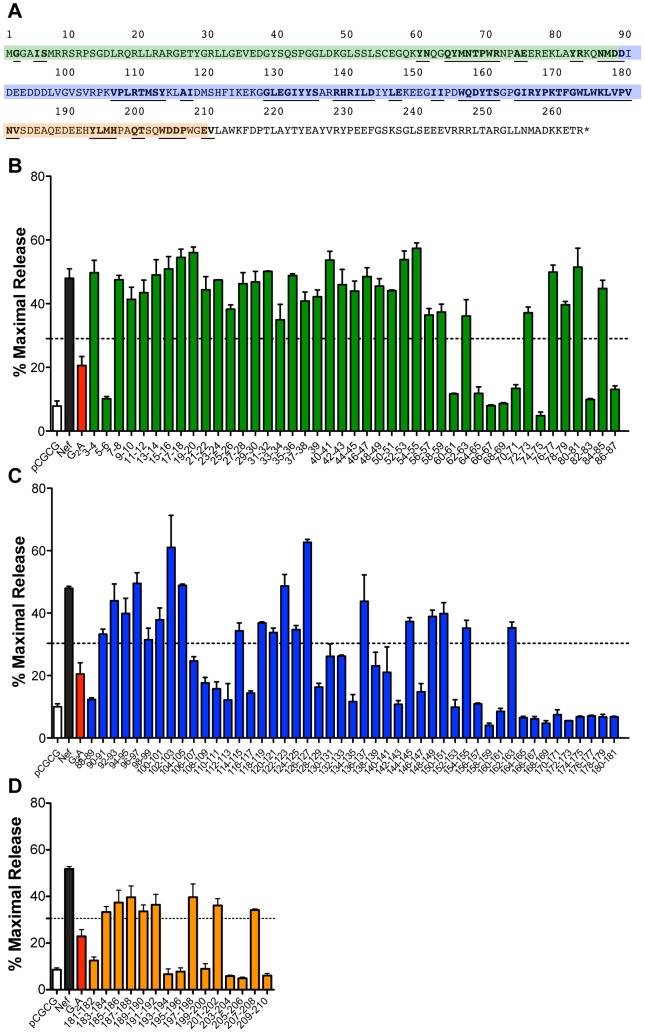
Figure 2. Identification of residues in SIV Nef necessary for tetherin antagonism.
(A) Predicted amino acid sequence of SIVmac239 Nef. The highlighted sequences correspond to the N-terminal domain (green), the globular core (blue), and the flexible loop region (orange). Substitutions in residues that impaired tetherin antagonism are underlined and in bold. (B, C and D) 293T cells were co-transfected with SIV Δnef proviral DNA together with constructs expressing rhesus tetherin and either wild-type or mutant Nef proteins. The percentage of virus release was determined by measuring the accumulation of SIV p27 in the culture supernatant in the presence of tetherin relative to transfections with empty vector. Controls include virus release in the absence of Nef (pCGCG; white), wild-type Nef (black) and Nef with a glycine-to-alanine substitution in the myristoylation site (G2A; red). Substitutions in the N-terminal domain are indicated by green bars (B), substitutions in the globular core domain are indicated by blue bars (C), and substitutions in the flexible loop region are indicated by orange bars (D). Error bars represent the standard deviation of duplicate transfections and the dotted line indicates 3 standard deviations over the activity of the G2A mutant.