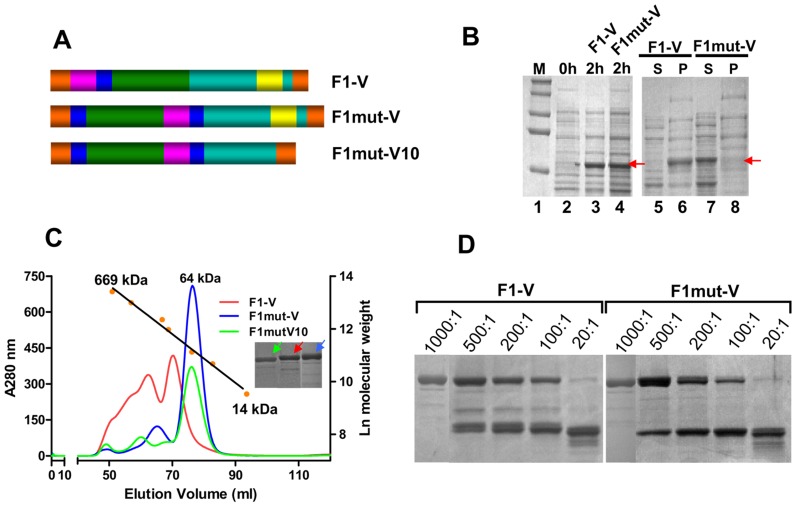
Figure 3. Construction of mutated F1-V immunogens.
(A) Schematic of native F1-V, F1mut-V and F1mut-V10. Cyan represents the coding sequence of V antigen, and yellow, the putative immunomodulatory sequence that is part of V sequence. Rest of the colors represents the same as described in legend to Figure 2. (B) Expression and solubility analysis of F1-V constructs were performed using the B-PER reagent. The samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. The positions of the F1-V protein bands are marked with red arrows. S, soluble fraction (supernatant from 12,000 g centrifugation of the lysate); P, insoluble fraction (pellet); M, molecular weight standards. (C) F1-V, F1mut-V and F1mut-V10 were purified by HisTrap column chromatography followed by Hi-load 16/60 Superdex 200 gel filtration. The calibration graph was generated by passing various molecular weight standards through the same column [Thyroglobulin (669 kDa), Ferritin (440 kDa), Catalase (232 kDa), aldolase (158 kDa), Ovalbumin (43 kDa), RNase A (14 kDa), and Albumin (67 kDa)]. The insert shows the purity of F1-V, F1mut-V, and F1mut-V10 proteins following SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining of the peak fractions. The color of arrows corresponds to the color of the elution profiles of various proteins. (D) Stability of F1-V and F1mut-V proteins was tested by treatment with increasing amounts of trypsin at room temperature overnight. The ratios shown above the gel correspond to the ratios of F1-V or F1mut-V proteins to trypsin (wt∶wt). See Materials and Methods for additional details.