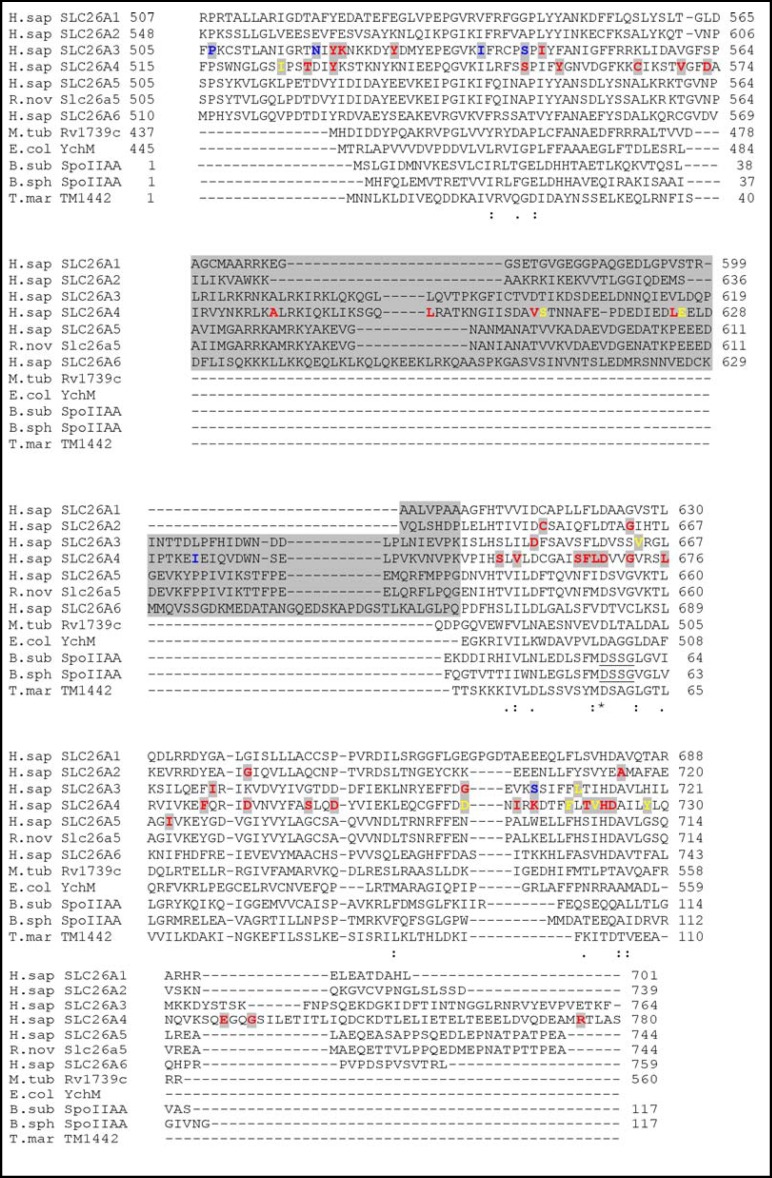
Fig. 8.
STAS domain amino acid sequences from the indicated human and rat SLC26 polypeptides, bacterial SulP proteins Rv1739c and YchM, and bacterial anti-anti-ρ pro teins SpoIIAA and TM1442. The anti-anti-ρ proteins are presented in their full lengths. Amino acid numbe ring is from UniProtKB (www.uniprot.org). The underlined DSSG motif of SpoIIAA includes its phosphorylated residue S58. Gray block indicates the intervening sequence (IVS) present in mammalian SLC26 STAS domains but absent from SulP STAS domains and from anti-anti- ρ proteins. SLC26 STAS amino acid residues in bold highlight human disease- associated missense mutations (in red), termination mutations (in yellow), and frameshifts mutations (in blue). Note that among SLC26 STAS domains, only in pendrin have mutations of the IVS been reported. Asterisks under sequences mark positions of complete sequence conservation. Alignment was generated by ClustalW2 (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalw2/).