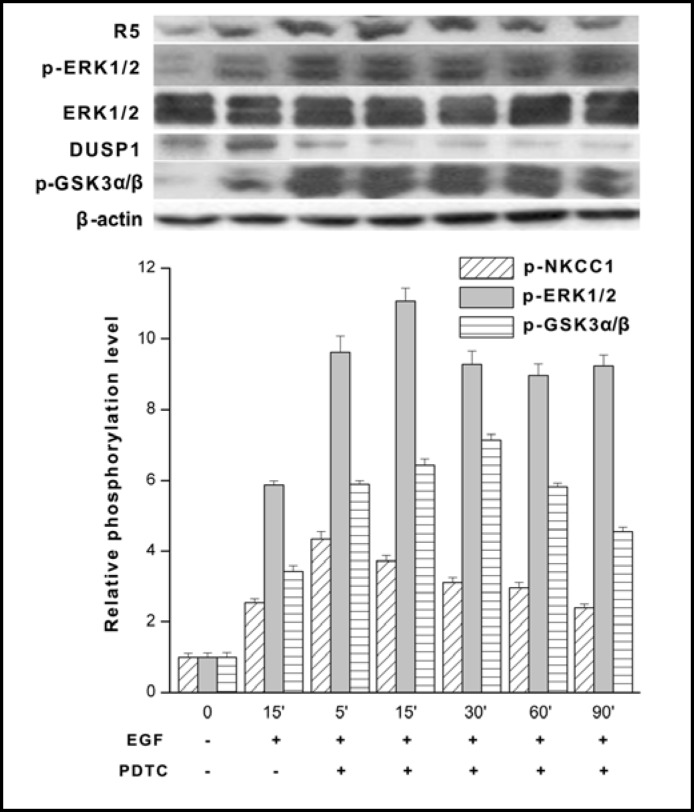
Fig. 10.
NF-kB inhibition prolongs EGF-induced ERK1/2 activation through downregulation of DUSP1 expression. HCEC were serum starved for 24 h at 80% to 90% confluence. Cells were exposed to 10 ng/ml EGF either in the presence or absence of 50 μM PDTC and cell lysates were obtained at each of the indicated times up to 90 min. The results obtained with PDTC following 15 min incubation and exposure to EGF for another 15 min are compared to those with EGF for up to 90 min without PDTC. Western blot analysis was performed with p-NKCC1, p-ERK1/2 and equivalent protein loading was confirmed with the anti ERK1/2 antibody. Under the same conditions individual changes in DUSP1 and p-GSK-3α/β expression detected with the appropriate antibody. Data represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. It is notable that PDTC exposure resulted in sustained p-ERK1/2 and p-NKCC1 formation over the 90 min (p<0.001 versus untreated control) period whereas declines in total DUSP1 exposure were accompanied by pronounced and continuous p-GSK3-a/β expression (p<0.05 versus untreated control). PDTC appears to inhibit GSK-3α/β through phosphorylation leading to declines in DUSP1 expression. Such declines account for sustained ERK1/2 phosphorylation due to loss of negative feedback control by DUSP1 of ERK1/2 activation.