Figure 4.
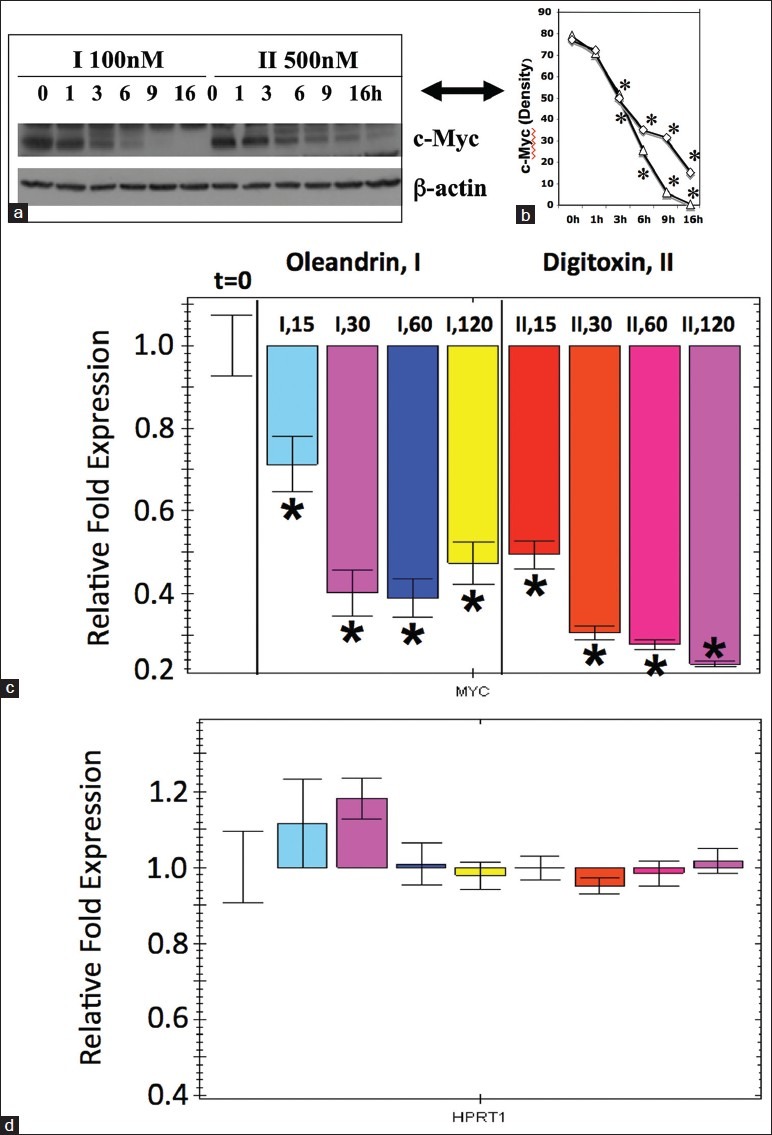
Cardiac glycosides induce rapid loss of c-MYC mRNA and protein. (a) Western blot analysis of c-MYC in cells treated with cardiac glycosides. Cells were treated with oleandrin (I, 100 nM) or digitoxin (II, 500 nM) for different times, at the concentrations shown. Western blot analysis was used to estimate levels of c-MYC remaining at each time point. The image is representative of three independent experiments.(b) Densitometric analysis of effect of cardiac glycosides on levels of immunoreactive c-MYC (Δ=I; ◊=II). Data are taken from the western blot data in a. Half-life of c-MYC in the presence of oleandrin or digitoxin is ca. 2-3 h. Differences are significant (*P < 0.05), relative to the 0-h time points. (c) Influence of cardiac glycosides on levels of c-MYC mRNA. Cells were treated with oleandrin (I, 100 nM) and digitoxin (II, 500 nM) for 15, 30, 60 and 120 min. C-MYC was quantitated by q-PCR (quantitative polymerase chain reaction) as described in the methods section. All data are statistically different from the 0-time condition on the extreme left hand side of the figure.(*P < 0.05). These data are representative of 3 independent experiments. (d) Influence of cardiac glycosides on levels of HPRT1 (hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoriribosyltransferase) in control mRNA. The same samples of RNA collected for the assay of c-MYC in c were also assayed by q-PCR for the HPRT1 mRNA. No statistically significant changes (*P < 0.05) were noted over the 2 h time period, in the presence of either oleandrin (I, 100 nM) or digitoxin (II, 500 nM). These data are representative of 3 independent experiments
