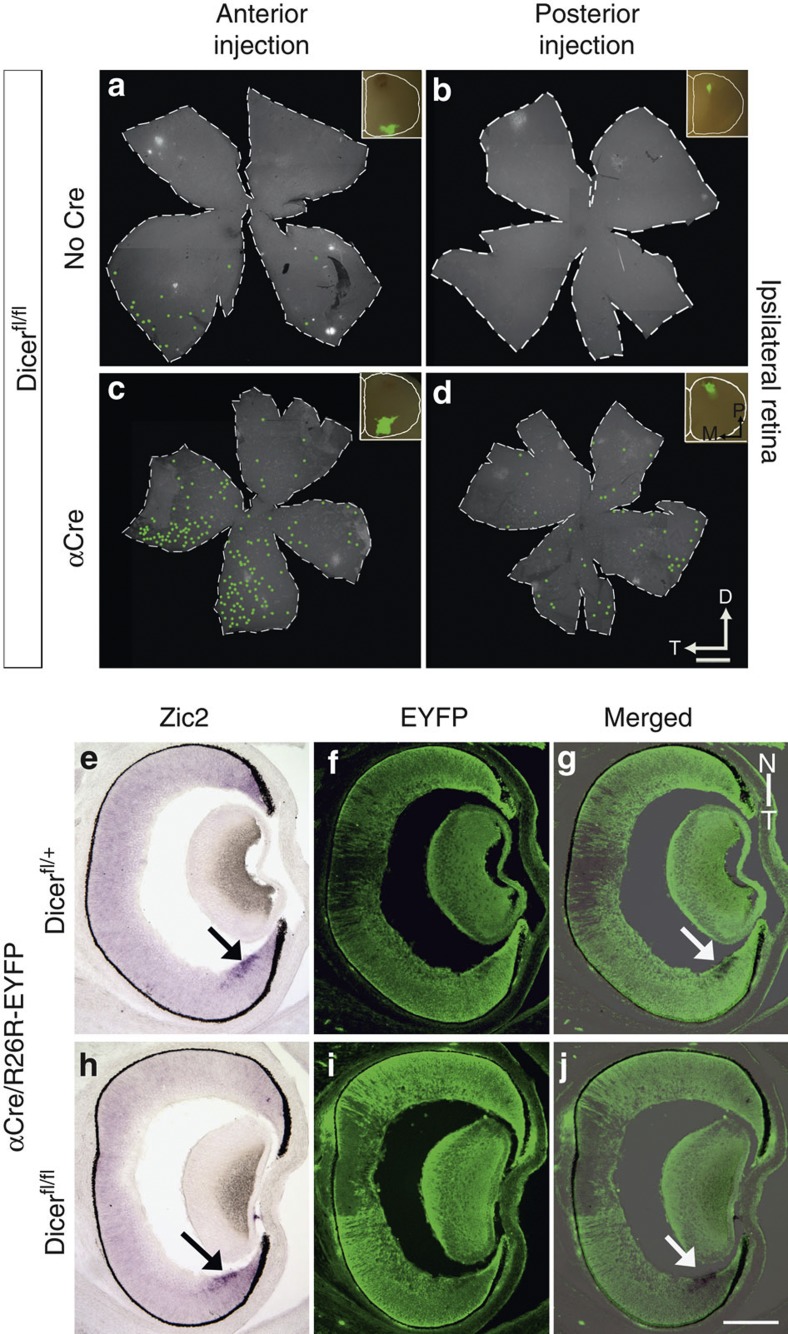
Figure 7. The origin of ipsilateral-projecting RGCs is not restricted to the ventral temporal crescent in α-Del animals.
(a–d) Whole retina flatmounts detecting RGCs after retrograde labelling using fluorescent microbeads focally injected in the ipsilateral SC of control (a,b) or α-Del mutant mice (c,d) at P8. (a,b) In wild-type controls only injections into anterior ipsilateral SC resulted in retrogradely labelled RGCs in the retina, restricted exclusively to the ventral temporal crescent (VTC) (n=3). No labelled RGCs were detected upon injections in posterior (insets) ipsilateral SC (n=11). (c,d) In α-Del mice injections into both, anterior (c) and posterior (d) ipsilateral SC lead to retrogradely labelled RGCs in the retina. They are generally scattered across the retina, but show a location preference for the ventral temporal retina for anterior injections (c, n=3) and nasal retina for posterior SC injections (d, n=10). (e–j) Panels show in situ hybridization using an antisense probe against Zic2 (purple) and immunohistochemical detection for EYFP (green) on E16 horizontal retinal sections, from control heterozygous (e,f) and mutant (h,i) mice. Merged images are shown in (g,j). Zic2-positive cells in the VTC (arrow) are located within the Cre-positive (EYFP+) retinal areas, which undergo degeneration in mutant mice at perinatal stages. D, dorsal; N, nasal; T, temporal; VTC, ventral temporal crescent. Scale bar, 500 μm (a,d) and Scale bar, 200 μm (e,j).