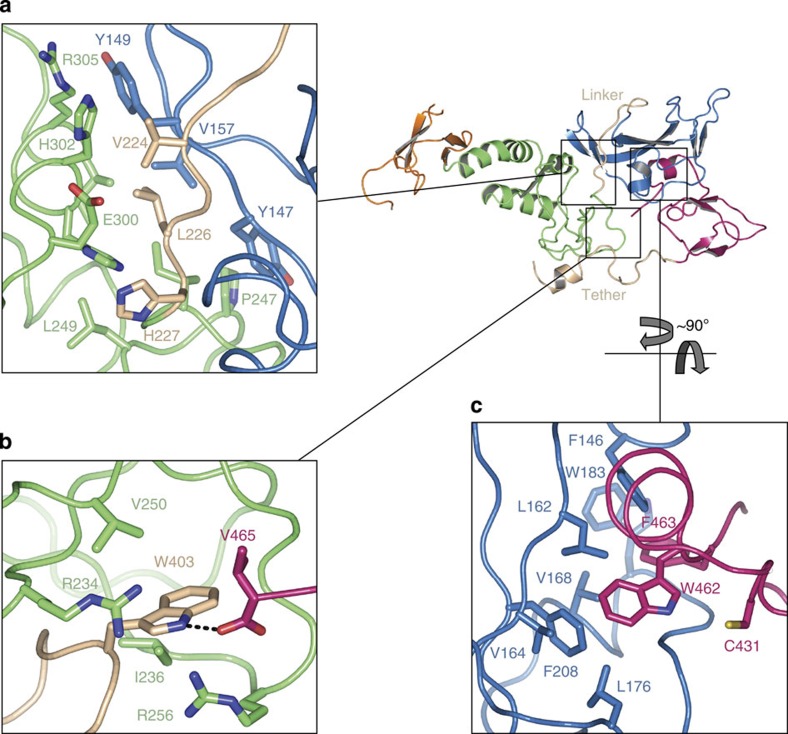
Figure 2. R0RBR is assembled into two compact domain groups separated by linkers.
(a) The R0 (blue) and R1 (green) interface is relatively hydrophilic and separated by the R0–R1 linker (beige), suggesting this area may have some structural flexibility. (b) The tether (beige) residue W403 sits in a hydrophobic pocket on R1 and may serve as a ‘pin’ to anchor the two turn helix of the tether to R1. W403 also forms a hydrogen bond with the terminal carboxylate of V465 (pink). R256 is the site of a human PD mutation. (c) The R0 (blue) domain forms a hydrophobic interface with the catalytic domain R2 (pink), inserting residues W462 and F463 into the hydrophobic core of R0. The catalytic cysteine, C431, is adjacent to this interface.