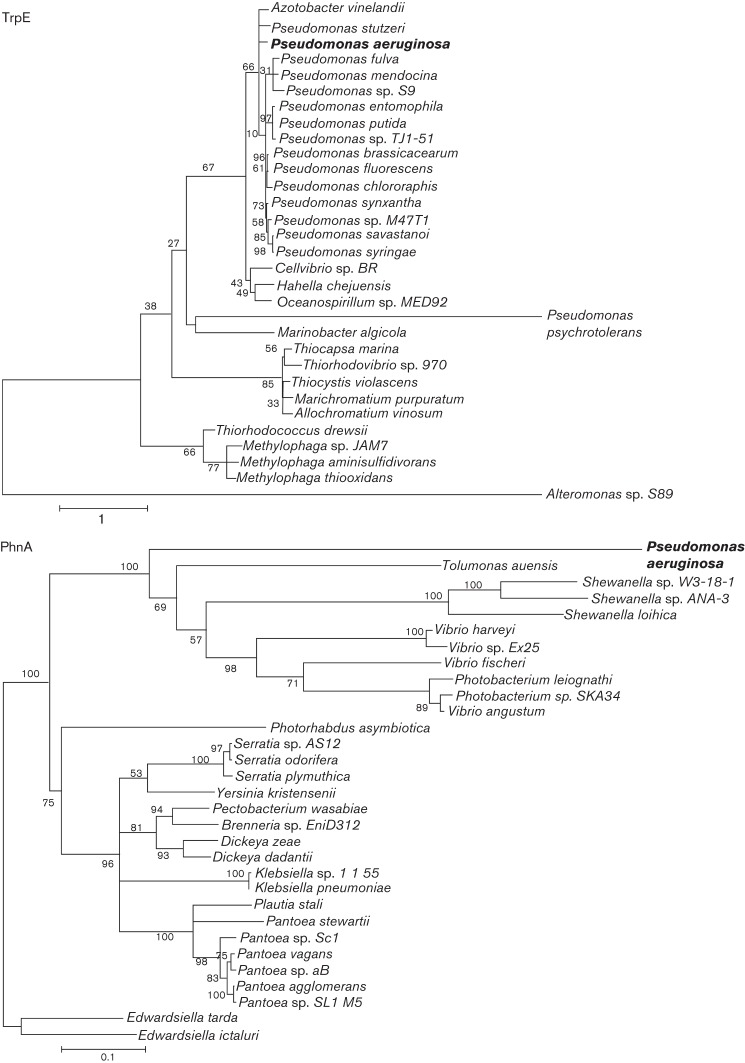
Fig. 1.
Anthranilate synthase phylogenetic trees. The top 30 homologues identified by blast analysis using the P. aeruginosa TrpE and PhnA sequences reveal the evolutionary relationships of each anthranilate synthase enzyme to those of other species. TrpEG are most closely related to anthranilate synthases from other members of the fluorescent pseudomonad family, while PhnAB are most closely related to anthranilate synthases from more distantly related organisms. The absence of a phnAB-like operon in other pseudomonads is evidence that PhnAB acquisition occurred after the family’s diversification. Bootstrap values at tree nodes indicate likelihood the node represents a genuine phylogenetic relationship.