Fig. 5.
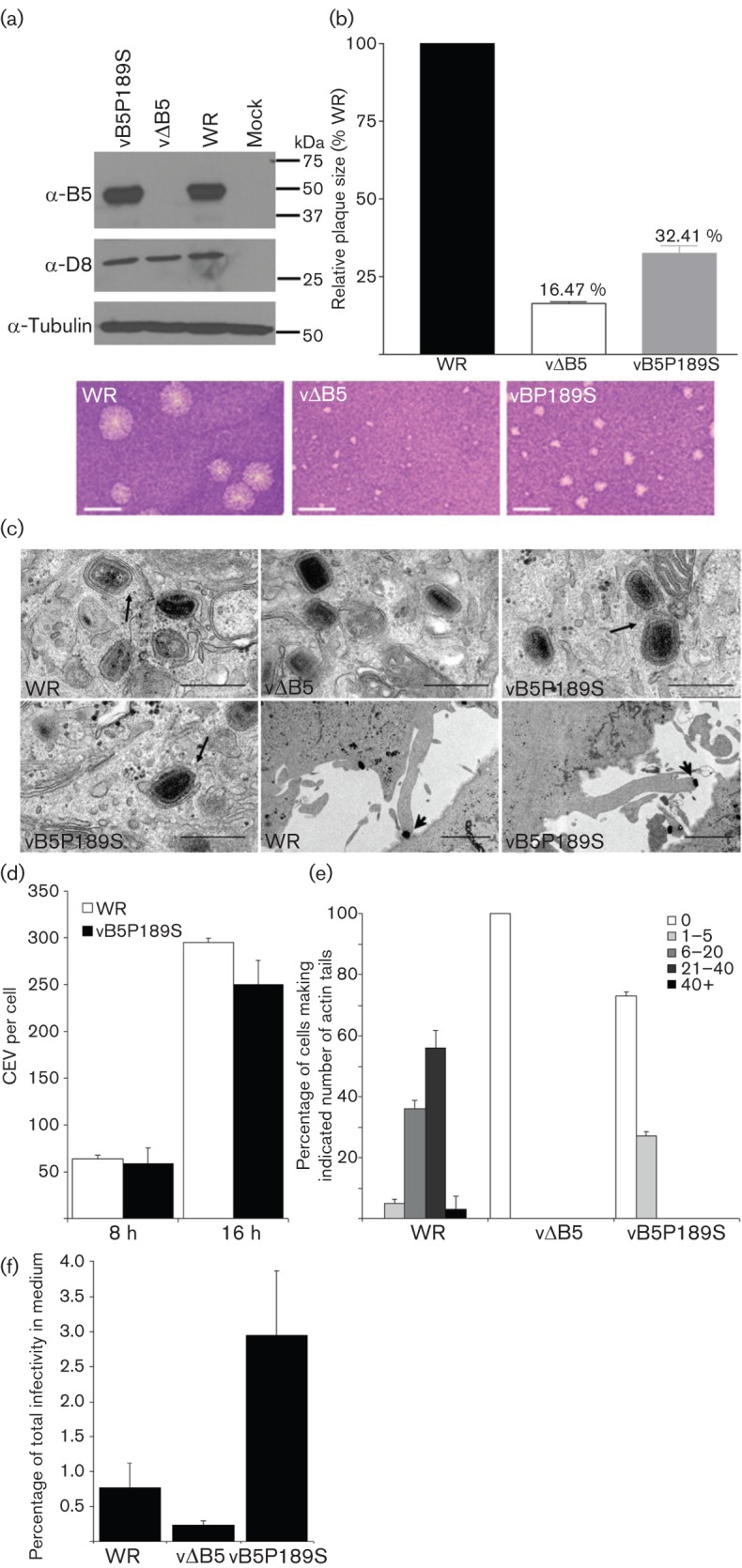
Characterization of rVACV vB5P189S. (a) Immunoblot. Lysates from BSC-1 cells infected with WR, vΔB5 or vB5P189S at 2 p.f.u. per cell were immunoblotted with anti-B5 mAb. (b) vB5P189S forms small plaques. BSC-1 cells were infected with WR, vΔB5 or vB5P189S and plaque size was measured after 3 days. Data are expressed relative to VACV WR and are the mean±sd, n = 3. Bars, 2.5 mm. (c) Electron microscopy of HeLa cells infected with WR, vΔB5 and vB5P189S at 2 p.f.u. per cell for 8 h. Black arrows indicate IMV association with wrapping membranes and complete IEV. Arrowhead indicates a virus-tipped actin tail at the surface of cells infected with vB5P189S. Bars, 500 nm (all top row and bottom row left), 2 µm (bottom row middle and right). (d) CEV formation. BSC-1 cells were infected as in (a) and CEV were quantified on cells in 9–10 different fields for each virus. Data shown are the mean±sd of three experiments. (e) Actin-tail production. RK13 cells were infected as in (a) and 16 h p.i. cells were fixed, permeabilized and stained with phalloidin and an anti-D8 mAb. The number of actin tails present at the surface of 50 cells was determined for each virus and classified into five categories: 0, 1–5, 6–20, 21–40 or >40 actin tails. Data shown are the mean±sd, n = 2. (f) Extracellular virus formation. RK13 were infected at 5 p.f.u. per cell for 24 h and the number of infectious virions present intracellularly and extracellularly was determined by plaque assay. Data are shown as the percentage of total infectivity that was present in the medium and are the mean±sd, n = 3.
