Fig. 3.
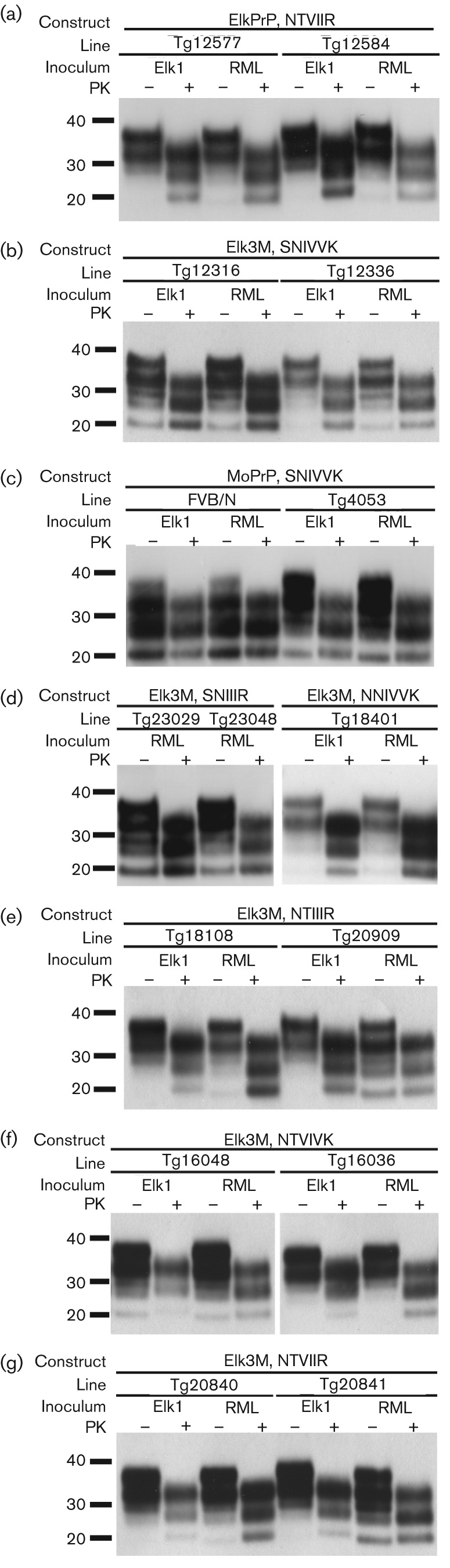
Western blot analyses of brain homogenates of mice following inoculation of Elk1P prions and RML prions. (a) Tg(ElkPrP)12577 and Tg(ElkPrP+/+)12548 mice expressing ElkPrP. (b) Tg(Elk3M,SNIVVK)12316 and Tg(Elk3M,SNIVVK)12336 mice expressing Elk3M with mouse residues (SNIVVK) at all six C-terminal positions. (c) FVB/N and Tg(MoPrP)4053 mice expressing MoPrP. (d) Tg(Elk3M,SNIIIR)23029 and Tg(Elk3M,SNIIIR)23048 mice expressing Elk3M with three mutations to ElkPrP, and Tg(Elk3M,NNIVVK)18401 mice expressing Elk3M with the S173N mutation. (e) Tg(Elk3M,NTIIIR+/+)18108 and Tg(Elk3M,NTIIIR)20909 mice expressing Elk3M with five mutations to ElkPrP. (f) Tg(Elk3M,NTVIVK)16048 and Tg(Elk3M,NTVIVK)16036 mice expressing Elk3M with four mutations to ElkPrP. (g) Tg(Elk3M,NTVIIR)20840 and Tg(Elk3M,NTVIIR)20841 mice expressing Elk3M with all six mutations to ElkPrP. In all panels, samples were either subjected to limited digestion with PK (+) or left undigested (−). Blots were probed using recFab HuM-P coupled to HRP. Apparent molecular masses based on migration of protein standards are shown in kDa.
