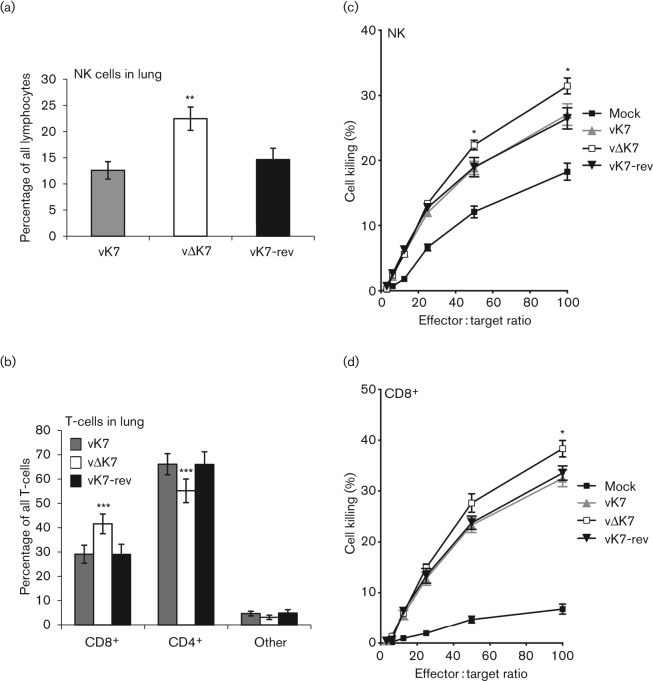
Fig. 7.
vΔK7 induces augmented intrapulmonary cytolysis by NK and CD8+ T-cells. BALB/c mice (n = 5 per group) were infected i.n. with the indicated viruses at 7×103 p.f.u. per mouse and lung tissue was harvested on day 6. Flow cytometry was used to define the percentage of NK cells (CD3−, DX5+; expressed as a proportion of all lymphocytes) (a) and T-cell subsets CD4+ and CD8+ (expressed as a proportion of all T-cells) (b). Chromium-release cytotoxicity assays were performed using total lung cell suspensions as effector cells. Yac-1 cells were used as NK cell targets (c) and VACV-infected P815 cells were used as CD8+ T-cell targets (d). Data are presented as mean±sd for cytometry (a, b) and mean±sem for cytotoxicity assays (c, d). Asterisks indicate significant difference between vΔK7 and other viruses: *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001.