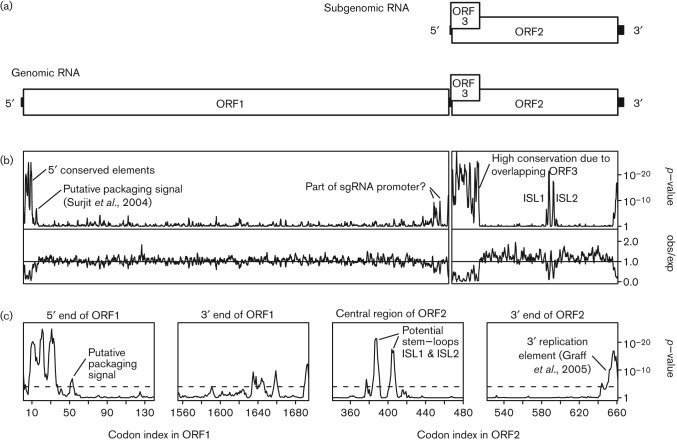
Fig. 1.
HEV genome organization. (a) Map of the ~7.2 kb genome. ORF1 is translated from the genomic RNA and encodes the replication protein domains including the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. ORF2 and ORF3 are translated from a sgRNA. ORF2 encodes the capsid protein. (b) Conservation at synonymous sites in alignments of 185 ORF1 and 205 ORF2 nucleotide sequences, using a 5-codon sliding window. The putative packaging signal is according to Surjit et al. (2004). The lower panels show the ratio of the observed number of substitutions to the number expected under a null model of neutral evolution at synonymous sites, while the upper panels show the corresponding P-values. In order to map the conservation statistic onto the coordinates of a specific sequence in the alignment, all alignment columns with gaps in a chosen reference sequence (viz. NC_001434) were removed (note that the ORF2 alignment had no gaps in the reference sequence). Note, as expected, the extreme reduction in ORF2-frame synonymous substitutions in the region where ORF2 overlaps with ORF3. (c) Zoom-in of four regions that show particularly pronounced conservation at ORF1- or ORF2-frame synonymous sites. The dashed line indicates a P = 0.05 threshold after applying a rough correction for multiple testing (viz. 0.05/[2355 codons/5-codon window] ~ 1.1×10−4).