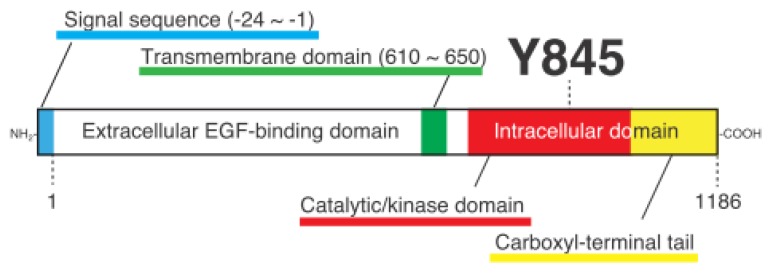
Figure 1.
Schematic structure of EGFR. The translational protein product of the human EGFR consists of a single polypeptide of 1210 amino acids. Upon protein maturation that involves extensive glycosylation of the amino-terminal EGF-binding extracellular domain, the amino-terminal 24 amino acids are removed as a signal sequence (as indicated by a blue area), by which the mature protein becomes a polypeptide of 1186 amino acids. In addition to the extracellular domain, EGFR contains a single transmembrane domain at almost the center of the protein (green) and a carboxyl-terminal sequence that contains the catalytic/kinase domain (red) and a non-catalytic tail sequence (yellow), between the two where the Src phosphorylation site Y845 and several tyrosine residues to be autophosphorylated are located.