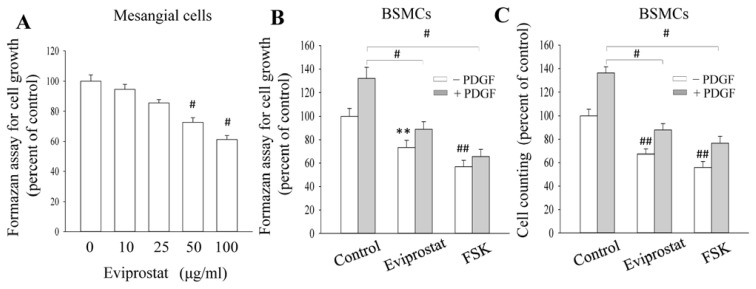
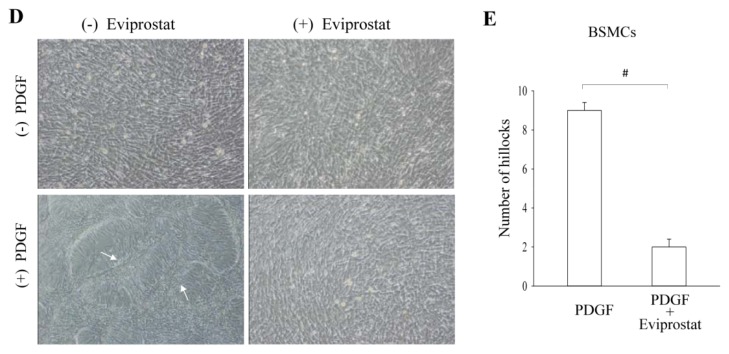
Figure 4.
Anti-proliferative effect of Eviprostat. (A) Dose-dependent effects of Eviprostat on mesangial cell proliferation. Mesangial cells were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of Eviprostat for 1 h before exposing to 20 ng/mL platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) for 24 h. Cell growth was evaluated by formazan assay. The data were expressed as percent of the control at zero point (mean ± SE, n = 4), # p < 0.01 vs. zero point control. (B and C) Effects of Eviprostat and forskolin (FSK) on bladder smooth muscle cells (BSMCs) proliferation. BSMCs were treated with 50 μg/mL Eviprostat or 10 μM FSK for 1 h before incubation with 20 ng/mL PDGF for an additional 24 h. Cell growth was determined by either formazan assay (B) or direct cell counting (C). The data were expressed as percent of untreated control (mean ± SE, n = 4); # p < 0.01 vs. PDGF alone, ** p < 0.05 and ## p < 0.01 vs. untreated control. (D and E) Effect of Eviprostat on hillock formation. BSMCs were pretreated with 50 μg/mL Eviprostat for 12 h or left untreated and exposed for 20 ng/mL PDGF for additional 48 h. The cell morphology was photographed (C, magnification: 200×), and the number of hillocks was manually counted in a blind manner and were shown in D. Results were expressed as the average number of hillocks counted in ten fields. # p < 0.01 vs. PDGF alone. Arrows denote multilayered ridges and nodules, the characterized feature of hillocks.