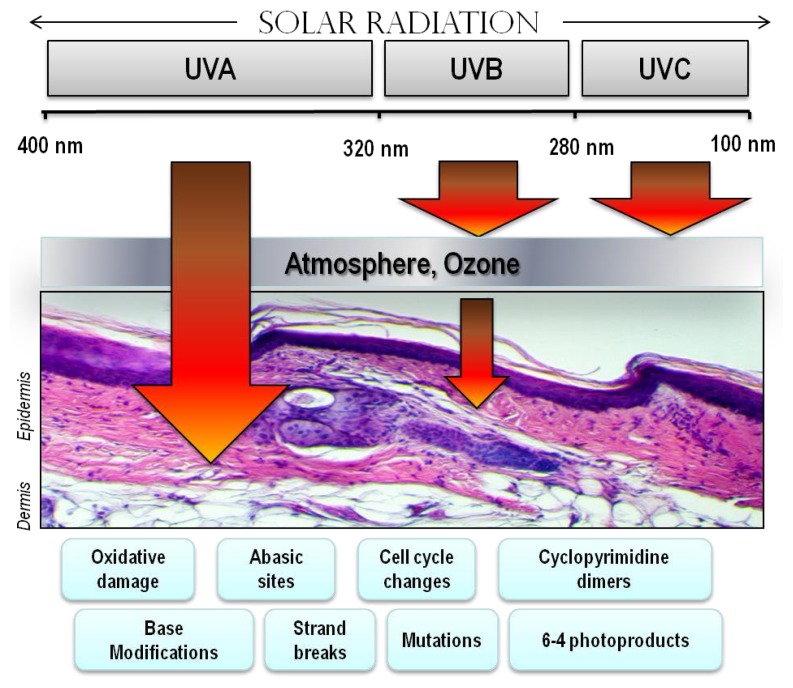
Figure 3.
Electromagnetic spectrum of visible and UV radiation and biologic effects on the skin. Solar UV radiation can be subdivided into UVA, UVB and UVC components, however because of atmospheric ozone that absorbs UVC, ambient sunlight is predominantly UVA (90%–95%) and UVB (5%–10%). UV penetrates the skin in a wavelengthdependent manner. Longer wavelength UVA penetrates deeply into the dermis reaching well into the dermis. In contrast, UVB is almost completely absorbed by the epidermis, with comparatively little reaching the dermis. UVA is efficient at generating reactive oxygen species that can damage DNA via indirect photosensitizing reactions. UVB is directly absorbed by DNA which causes molecular rearrangements forming the specific photoproducts such as cyclobutane dimers and 6–4 photoproducts. Mutations and cancer can result from many of these modifications to DNA.