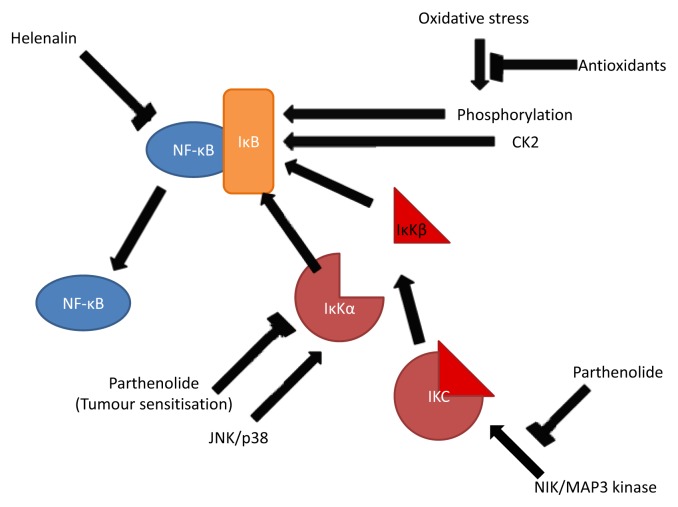
Figure 2.
Activation and inhibition of NF-κB by different hypothesized interactions with parthenolide or helenalin. Parthenolide can act to alkylate IKC preventing a cell signaling cascade by NIK or MAP3 kinase stimuli, whereas helenalin is thought to directly modify the p65 subunit of NF-κB, inactivating the molecule. Tumor sensitization has been attributed to many varied mechanisms often unrelated to the NF-κB molecule, though it is postulated that one mechanism is via phosphorylation of IκB thus preventing deactivation by IκK.