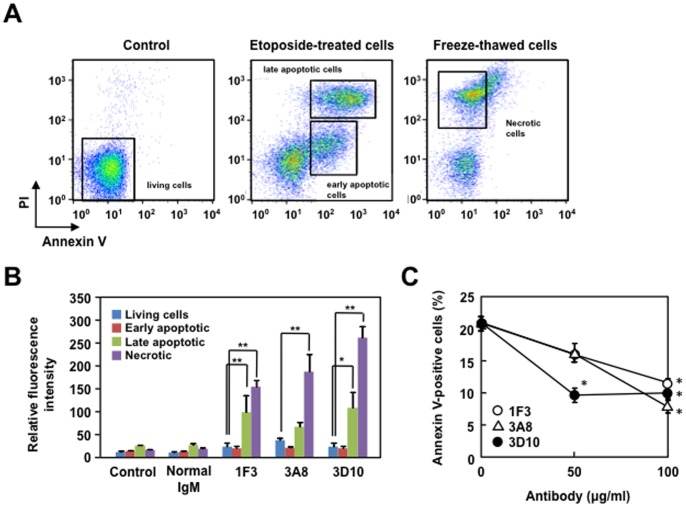
Figure 7. The binding of the ONE-specific IgM mAbs to the apoptosis-induced cells evaluated using Annexin-V/PI.
(A) Apoptosis-induced Jurkat cells were incubated with monoclonal antibodies and gated into populations according to the Annexin V and PI intensity; early apoptotic cells (single positive in Annexin-V but not PI) and late apoptotic and necrotic cells (double positive in Annexin-V/PI staining). Necrosis in Jurkat cells was induced by a freeze-thawing. (B) Bar graph representing relative fluorescence intensity of antibody binding to living cells, early apoptotic cells, late apoptotic cells, and necrotic cells. The non-immune control murine IgM and the ONE-specific IgM mAbs, 1F3, 3A8, and 3D10, isolated from the MFG-E8−/− mice, were used. The means were tested for statistical significance by using Tukey’s HSD test, assuming equal variances. Statistically significant differences between the relative fluorescence intensity of living cells are indicated by asterisks (*, P<0.05; **, P<0.01). (C) Inhibition of Annexin-V binding to apoptotic Jurkat cells by the ONE-specific IgM mAbs. The apoptosis-induced Jurkat cells were incubated with the ONE-specific IgM mAbs (0, 50, and 100 µg/ml) and Annexin-V and the binding of Annexin V to the cells was analyzed by flow cytometry.