FIG. 1.
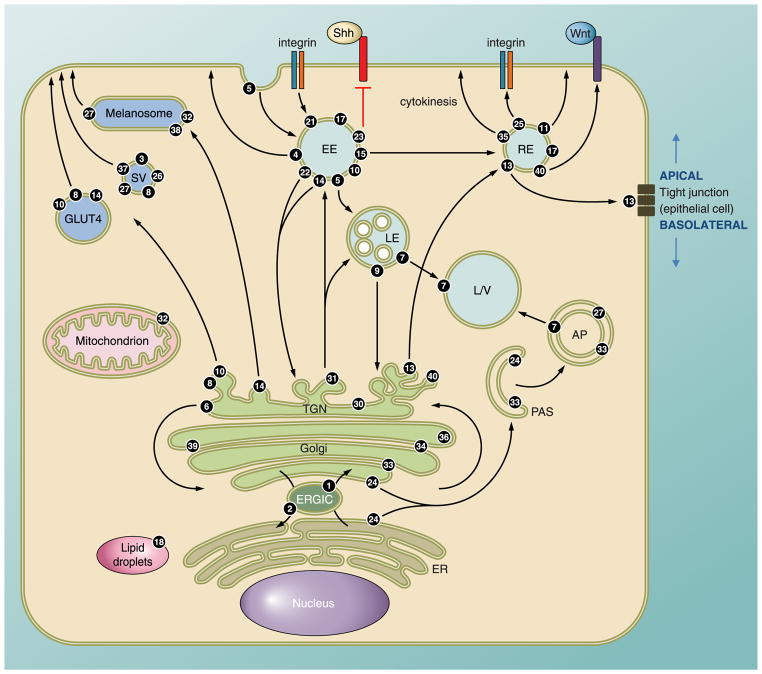
The intracellular localization of Rabs. A typical cell showing the intracellular localization and associated vesicle transport pathway(s) of several Rab GTPases. Rab1 regulates ER-Golgi traffic while Rab2 is involved in recycling, or retrograde traffic, from Golgi and the ERGIC back to the ER. Rab6 regulates intra-Golgi traffic. Several Rabs including Rab8, -10, and -14 regulate biosynthetic traffic from the trans-Golgi network (TGN) to the plasma membrane. The glucose transporter GLUT4 is found in vesicles that use these Rabs to reach the plasma membrane. Several secretory vesicles and granules use Rab3, -26, -27, and -37 to exocytose their cargo. Rab27 is well-studied in the melanosome transport that also relies on Rabs 32 and 38. There are numerous Rabs associated with endosomal traffic, and the most active site of localization is the early endosome. Most early endocytic steps rely on Rab5, which mediates fusion of endocytic vesicles to form the early endosome. Traffic can be directed towards the lysosome for degradation, which relies on action of Rab7, or to various recycling compartments to return factors to the plasma membrane. Rab15 directs membrane traffic from the early endosome to the recycling endosome. Rab4 and Rab11 regulate fast and slow endocytic recycling, respectively. Specialized Rab functions include Rab18-mediated regulation of lipid droplets, intracellular lipid storage sites. Rab24 and Rab33 mediate formation of the preautophagosomal structure that engulfs cellular components to form the autophagosome that is subsequently targeted to the lysosome/vacuole. Rab21 and Rab25 regulate transport of integrins to control cell adhesion and cytokinesis. Rab13 directs traffic to and regulates formation of tight junctions in polarized epithelial cells. Tight junctions define the boundary between the apical and basolateral regions of the polarized cell. Mutations in the mouse Rab23 gene lead to a severe developmental defect, open brain, because Rab23 acts downstream to negatively regulate Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling during dorsoventral development of the mouse spinal cord. It potentially interacts with the transcription factors activated by the Shh pathway. Rab40 also acts in a signaling pathway; it recruits components of the ubiquitination machinery to regulate Wnt signaling. There are several poorly characterized Rabs, such as Rab35. It controls plasma membrane recycling of an essential factor in cytokinesis. Rab34 and Rab39 are found on the Golgi, but it is unclear what role they play. AP, autophagosome; ERGIC, ER-Golgi intermediate compartment; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; EE, early endosome; LD, lipid droplet; LE, late endosome (multivesicular body); L/V, lysosome/vacuole; PAS, preautophagosomal structure; RE, recycling endosome; SV, secretory vesicle/granule.