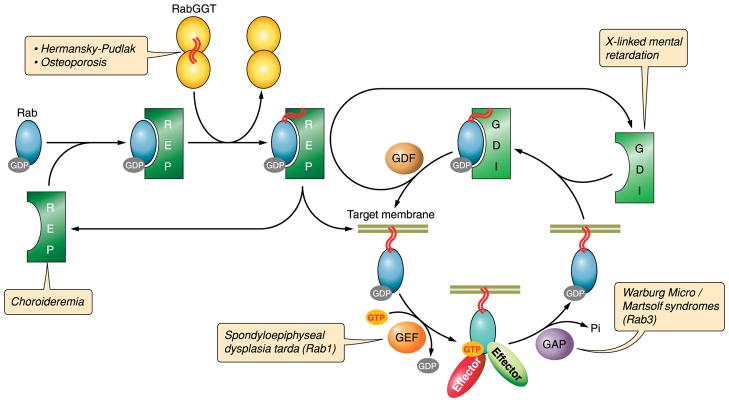
FIG. 2.
The Rab cycle. The newly synthesized Rab protein associates with Rab escort protein (REP) that directs it to Rab geranylgeranyl transferase (RabGGT) to receive its prenyl tails (red wavy lines). REP delivers the Rab to its target membrane. Throughout this process, the Rab is GDP-bound. A guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) catalyzes exchange of GDP for GTP to activate the Rab. The GTP-bound Rab interacts with effector proteins that mediate membrane traffic in the pathway regulated by its associated Rab. The Rab then interacts with its associated GTPase activating protein (GAP) that catalyzes hydrolysis of GTP to GDP by the Rab. The Rab is then removed from the membrane by guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor (GDI) in preparation for the next cycle. The insertion of the Rab into the target membrane is mediated by a GDI dissociation factor (GDF) that releases the Rab from GDI. Loss-of-function mutations at each of the above steps produce disease phenotypes as indicated by the red text boxes.