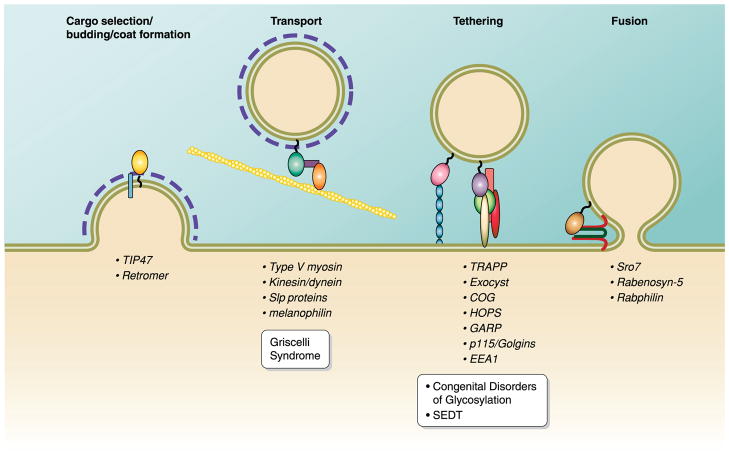
FIG. 3.
Rab effectors. Rabs perform their regulatory function by recruiting a variety of effectors to mediate different functions in membrane transport. These functions are as follows: 1) cargo selection/budding/coat formation, 2) vesicle transport, 3) vesicle uncoating/tethering, and 4) vesicle fusion. Below each function are examples of Rab effectors that perform said function. Mutations in Rab effectors also lead to disease phenotypes: Griscelli Syndrome is caused by mutations in either Rab27A, the Rab27A effector protein melanophilin, or myosin VA, while congenital disorders of glycosylation and spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda (SEDT) are caused by mutations in several COG subunits (COG1, COG7, and COG8) and the TRAPP subunit Trs20, respectively.