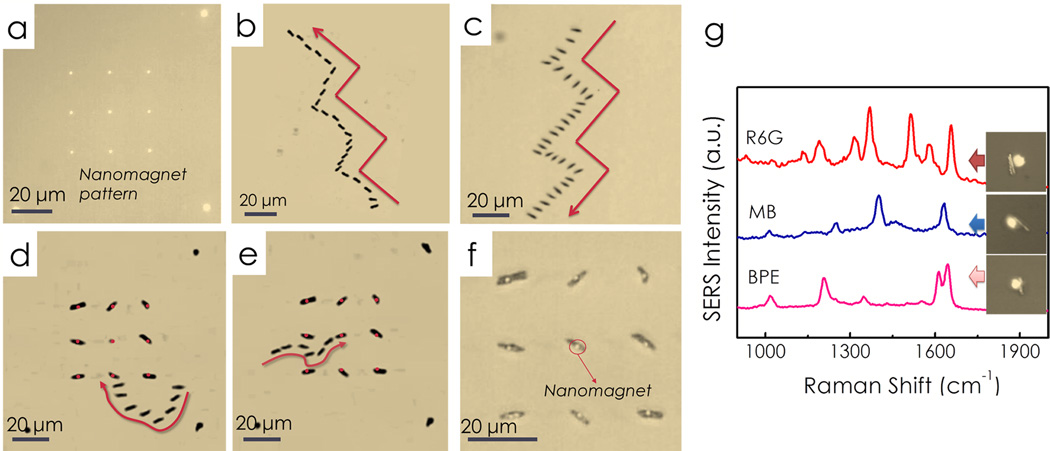
Figure 4.
Nanocapsules can be precisely transported and assembled on the nanomagnets with electric tweezers. (a) A 3×3 array of nanomagnets fabricated using E-beam lithography. With combined AC and DC E fields applied in both X and Y directions, nanocapsules were transported along prescribed trajectories such as “stairs” with (b) parallel and (c) transverse orientations. (d, e) Overlapped snapshots show the assembling process of a nanocapsule, where the nanomagnets were highlighted in red. The nanocapsules can be maneuvered and positioned at designated positions, showing the high flexibility and precision of the assembling. (f) An assembled 3×3 nanocapsules array. The bright nanomagnets are in the center of the nanocapsules, indicating that the attachment is due to the magnetic attraction between the Ni segments in the center of the nanocapsules and the magnetic layers in the patterned magnets. All the images were taken by reflective optical imaging. (g) From assembled nanocapsules, we have detected various chemicals including R6G, methylene blue, and BPE.