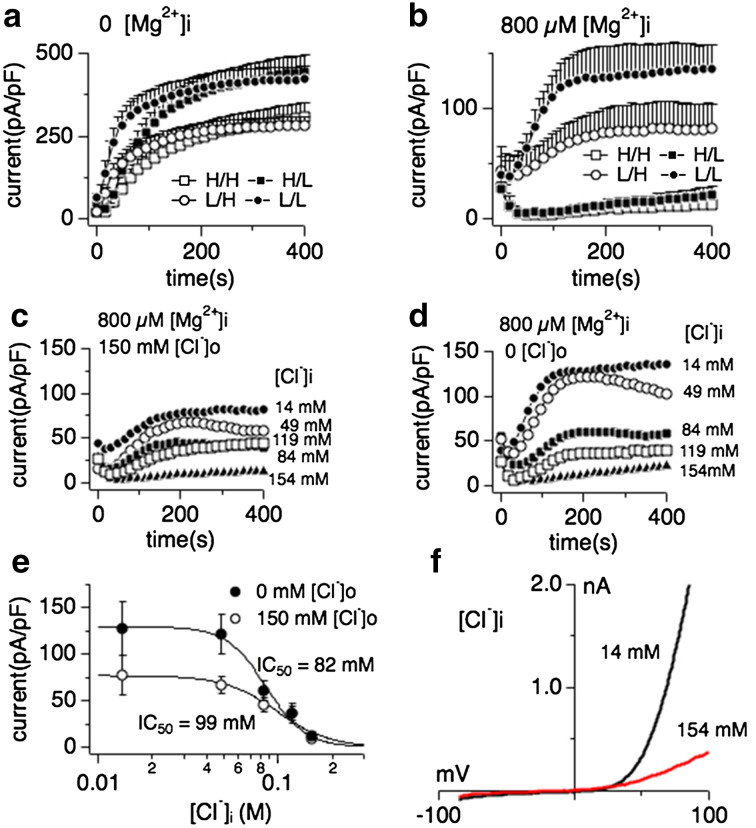
Fig. 1.
Intracellular Mg2+ is an obligatory co-factor of chloride-induced TRPM7 inhibition. Whole-cell currents were recorded in HEK293 cell induced to overexpress human TRPM7 (tetHEKTRPM7). Voltage ramps were from −100 to +100 mV over 50 ms time and given at an interval of 2 s. TRPM7 current amplitudes were assessed at +80 mV, averaged and normalized to cell size (in pF). In [H/H] conditions (open square), both intracellular and extracellular solutions contained high concentrations of chloride (154 mM each, see “Methods”), either in the form of CsCl (internal) or NaCl (external). In [H/L] conditions (filled squares), cells were perfused with high intracellular chloride (154 mM) solution and kept in low extracellular chloride (4 mM) solution (see “Methods”). In [L/H] conditions (open circles), cells were perfused with low intracellular chloride (14 mM) solution and high extracellular chloride solution. For [L/L] (filled circles), cells were perfused with low chloride both intracellularly and extracellularly. Intracellular free Mg2+ was either chelated to 0 mM (panel a) or clamped at 800 μM, the latter bringing internal chloride solutions to a total of 14 mM (panel b). Error bars indicate SEM a comparison of effects of intra- and extracellular Cl− on TRPM7 currents in the absence of intracellular Mg2+ (n = 6–8). b Comparison of intra- and extracellular Cl− on TRPM7 currents in the presence of intracellular 800 μM free Mg2+ (n = 6–8). c Inhibition of TRPM7 currents by increasingly higher intracellular Cl− concentrations in the presence of high extracellular chloride (154 mM; n = 6–8) and 800 μM intracellular Mg2+. d Inhibition of TRPM7 currents by increasingly higher intracellular Cl− concentration with cells kept in low chloride conditions (4 mM) by substituting NaCl with Na-gluconate. Intracellular Mg2+ was kept at 800 μM. e Dose–response curves for TRPM7 inhibition by increasing intracellular Cl− concentrations from data in panels C and D. Data points correspond to averaged, cell-size (in pF) normalized current amplitudes measured at +80 mV and at 200 s of whole-cell recording and plotted as a function of Cl− concentration (n = 6–8 each data point). The best fit was obtained by a Hill coefficient close to 3 and was therefore fixed at that value. The calculated IC50 value for Cl−-induced inhibition of TRPM7 currents with or without external Cl− is IC50 = 99 ± 9 mM (open circles) and 82 ± 6 mM (solid circles), respectively. Note the overall larger current under low external Cl− conditions. h Representative current voltage (I/V) relationships for TRPM7 in the presence of intracellular 14 or 154 mM Cl− taken from panel c