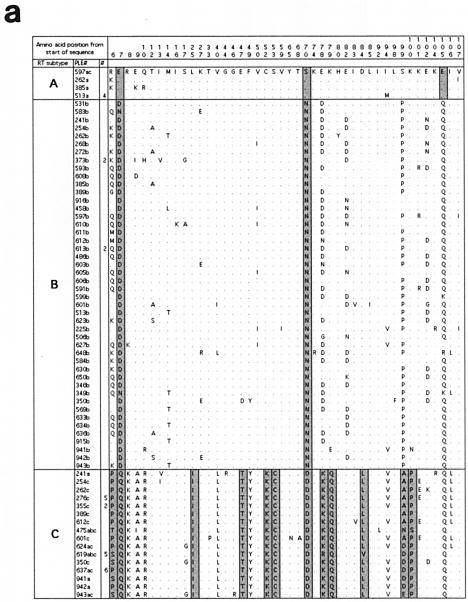
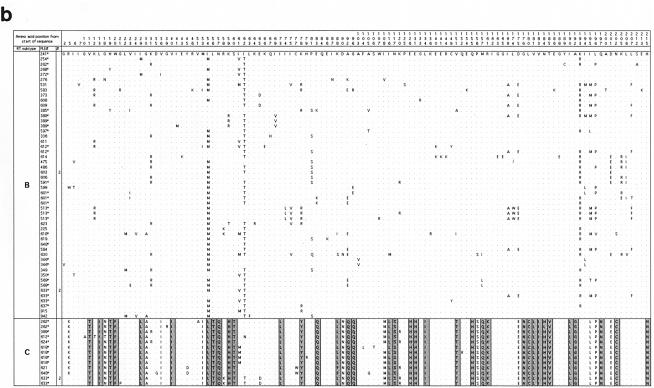
FIG. 2.
Alignments of the predicted amino acid translation products of FIV-Ple sequences from individual lions. Single-letter amino acid code was used. Only variable amino acids are included, and residues differing from the top sequence are shown. A dot designates identity with the top sequence. Dashed lines indicate gaps introduced to optimize the alignment. Sites that distinguish FIV-Ple RT-subtypes from each other are boxed, and fixed differences are shaded. In cases where more than one lion has identical FIV-Ple sequences, the number of lions (#) with that sequence is indicated. Cloned sequences are followed by an asterisk. (a) pol-RT translation products. The following lions had identical amino acid sequences: Ple-513, Ple-924, Ple-350, and Ple-626 (clade A); Ple-373 and Ple-609 (clade B); Ple-613 and Ple-614 (clade B); Ple-633 and Ple-637 (clade B); Ple-262 and Ple-610 (clade C); Ple-626, Ple-276, Ple-272, Ple-268, and Ple-923 (clade C); Ple-619, Ple-648, Ple-621, Ple-506, Ple-591, and Ple-618 (clade C); Ple-637, Ple-346, Ple-633, Ple-636, Ple-634, and Ple-569 (clade C); and Ple-355 and Ple-342 (clade C). (b) pol-RNase translation products. The following lions had identical amino acid sequences: Ple-603 and Ple-605 (clade B); Ple-633 and Ple-634 (clade B); and Ple-633, Ple-634, and Ple-636 (clade C). (c) gag translation products. The following lions had identical amino acid sequences: Ple-513 and Ple-913 (clade A); Ple-597 and Ple-601 (clade B); Ple-513 and Ple-623 (clade B); Ple-584 and Ple-648 (clade B); Ple-268, Ple-262, Ple-254, Ple-612, and Ple-618 (Clade C); and Ple-569, Ple-636, Ple-634, and Ple-633 (clade C).