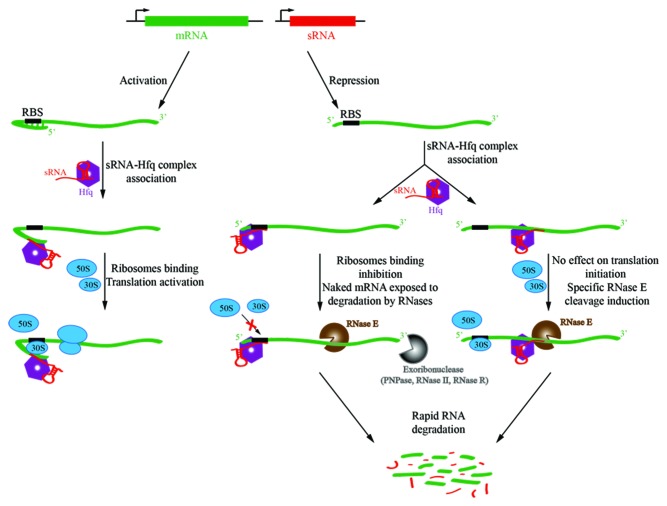
Figure 3. Schematic of small RNA (sRNA)-mediated regulation of gene expression. In the top panel, the sRNAs (red) are transcribed in trans to the target gene (green). A cognate seed region that pairs to a recognition site in the target RNA can relieve repression of translation by secondary structure that masks the ribosome-binding site (RBS, or Shine Dalgarno sequence). In this way, sRNAs can activate gene expression (left panel). Conversely, they can mask the RBS (ribosome binding site), thereby preventing translation initiation and making the naked RNA vulnerable to ribonuclease attack, as shown in the middle panel. sRNA can also bind within the coding sequence of the target mRNA and the sRNA 5′ end can allosterically activate RNase E to cleave target mRNA (right panel).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.