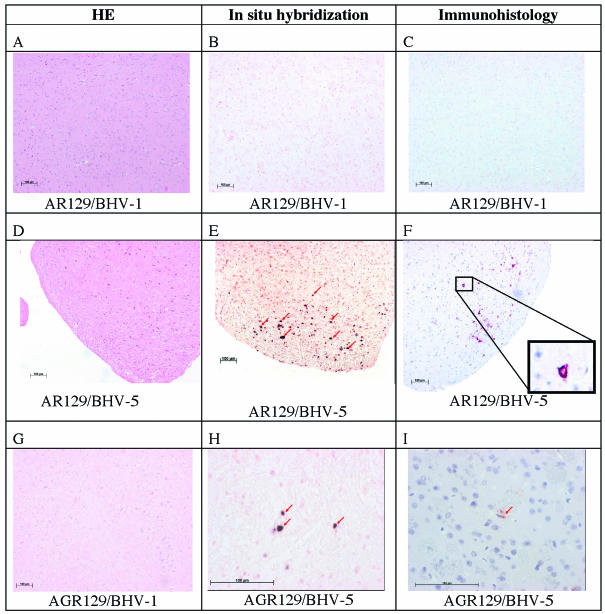
FIG. 4.
Analysis of mouse brains from BHV-1- and BHV-5-infected mice by histology, in situ hybridization, and immunohistology. AR129 (A to F) and AGR129 (G to I) mice were inoculated with BHV-1 or BHV-5 as indicated. At intervals, groups of mice were euthanatized to be analyzed at various time points after infection. (A, D, and G) Examples of histological examination following hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining at dpi 22 (A) or 16 (D and G), where no differences between various time points were recognized. (B, E, and H) Examples of results after in situ hybridization at dpi 22 (B), 16 (E) (arrows point to positive neuronal nuclei), or 11 (H). Viral DNA was not present at detectable levels in brain tissue collected from BHV-1-inoculated mice or in BHV-5-infected mice, before the onset of clinical symptoms (an example is shown in panel B). BHV-5 DNA detected by in situ hybridization is shown in panels E and H (arrows point to positive neuronal nuclei). (C, F, and I) Examples from immunohistological analyses at dpi 22 (C), 16 (F), and 11(I). Sections from BHV-1-inoculated mice and from BHV-5-infected mice, before the onset of clinical symptoms, reacted negatively (an example is shown in panel C). Structural glycoprotein C was detected by immunohistology following monoclonal antibody staining of brains from AR129 mice at dpi 16 after inoculation with BHV-5 (F) (the inset shows a positive neuron at a higher magnification) and from AGR129 mice at dpi 11 after BHV-5-infection (I) (the arrow points to a weakly positive cell that cannot be clearly identified as a neuron). Bars, 100 μm.