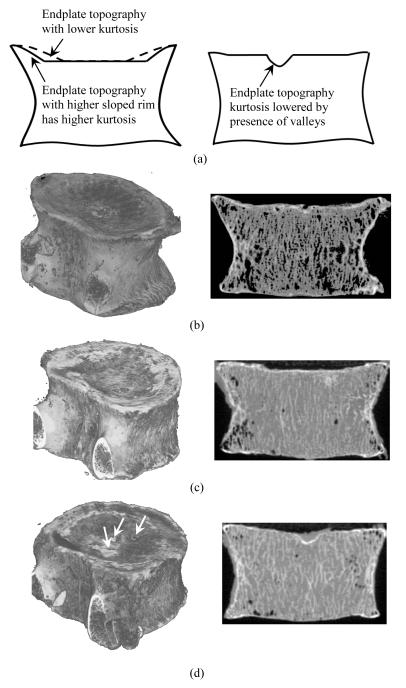
Figure 6.
Vertebrae with different inferior endplate surface topographies. (a) Illustration of cross sectional views of endplate topographies with different rim morphology (left) and presence of valleys on a relatively flat surface (right) resulting in kurtosis differences. (b) Kurtosis of inferior endplate topography=3.8. Presence of highly sloped rim and a large flat central surface area results in relatively high kurtosis. (c) Kurtosis of inferior endplate topography=2.3. Low sloped rim results in decrease of flat central surface area and low kurtosis compared to that in figure a. (d) Kurtosis of inferior endplate topography=2.2. Presence of valleys (indicated by arrows) on a relatively flat surface with no significant rim result in a low level of kurtosis.