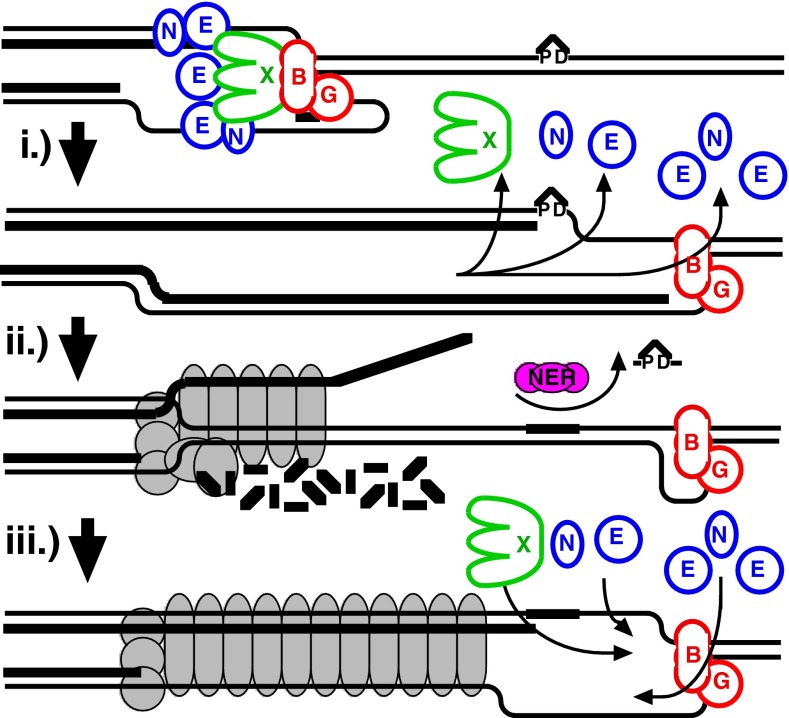
Fig. 5.
Model of replisome at UV-induced damage. Upon encountering an arresting lesion (PD, pyrimidine dimer) (i), DNA synthesis becomes uncoupled and the polymerases transiently dissociate. (ii) This serves as a signal to initiate the replication fork DNA processing by the RecF-pathway gene products (gray circles) allowing repair enzymes (NER) or translesion polymerases to access the lesion. (iii) The helicase–primase complex remains bound to the template DNA and serves to maintain the licensing and integrity of the replication fork, directing replisome reassembly to the correct location once the lesion has been processed.